Windows Audit Files and Folders allow you to track every activity that occurs in those files and folders for a variety of reasons.
There are many reasons to track the activity of files and folders in Windows. One of the most common reasons is the security issue to guarantee the integrity of the system. By enabling auditing of files and folders, you will know when users are accessing, reading, creating, modifying, or deleting files and folders.
If you’re an “Admin,” you can choose to allow specific users to track changes to files and folders and manage their access.
Tracking the creation and deletion of files and folders is mandatory to ensure data security and meet compliance mandate requirements. It also helps administrators to monitor files and folders in their system.
In case of a security attack, if the hacker deletes a file or folder, it will be easier to track it during the investigation.
One of the most effective methods to maintain the integrity of your system is security auditing. You should select the audit level for your environment as part of your overall security plan. The purpose of the audit is to find threats to your network, whether successful, as well as threats to resources that you have identified as important in your risk assessment.
How to enable Audit Files and Folders in Windows 11
There are several steps you have to do to enable audit files and folders. The stages are:
- Enable Object Access Auditing in the Group Policy.
- Configure Auditing on a File or Folder.
- Viewing and Analyzing Logs.
A. Enable Object Access Auditing in the Group Policy.
- Open the “Local Group Policy Editor“. You can open it by clicking the Windows Start button and typing “gpedit. Then click “Edit group policy” in the search box.
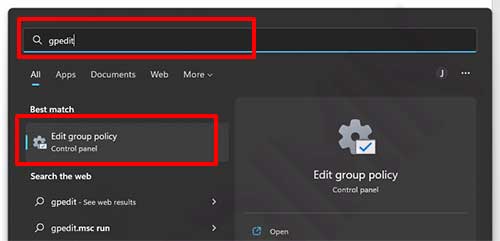
- Then in the Group Policy Editor window, navigate to “Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Audit Policy. Next on the right side, configure “Audit object access” by double-clicking.
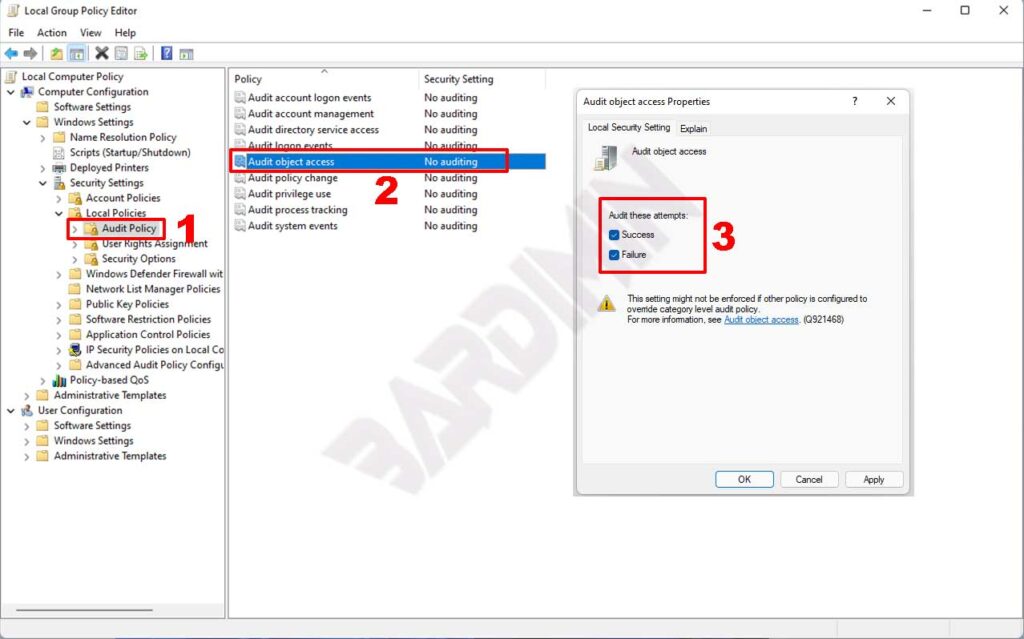
- In the “Audit object access Properties” window, check all the “Success” and “Failure” options to audit each attempt.
- Then Click the OK button and close the Local Group Policy Editor.
B. Configure Auditing on a File or Folder.
- Open File Explorer, then select the File or Folder you want to audit. Once you’ve selected it, right-click on it and select the “Properties” option.
- Next in the Properties window, select the “Security” tab. And on the tab, click on the “Advanced” button.
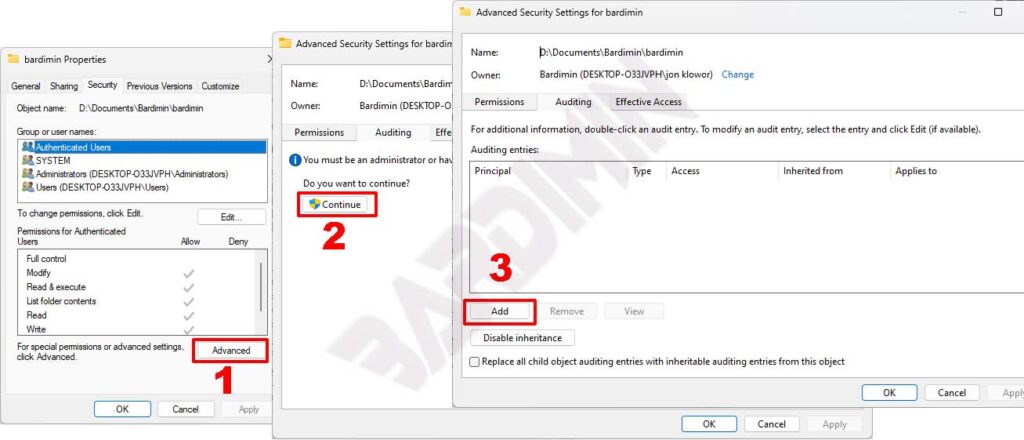
- Then it will open the “Advanced Security Settings” window and select the “Auditing” tab. Click the “Continue” button.
- After that, click on the “Add” button.
- The “Auditing entry” window will open and click “Select a principal“.
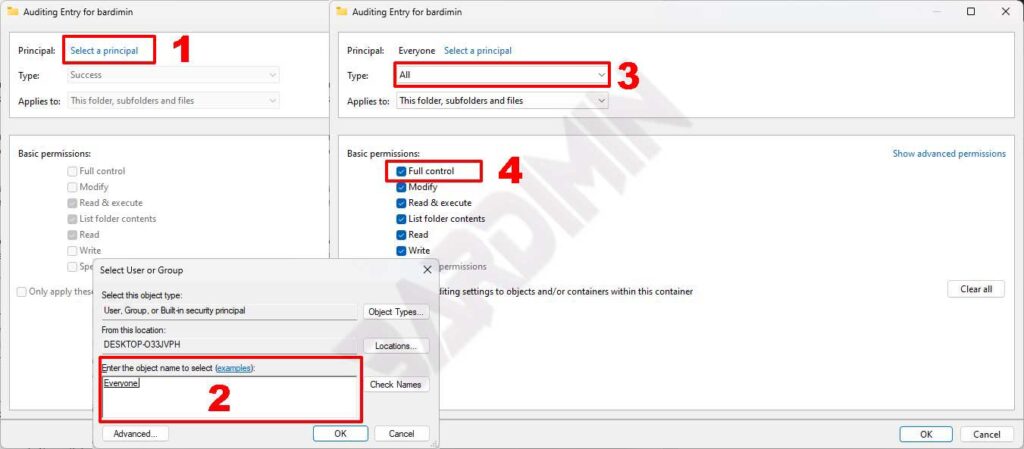
- Next, you will be asked to choose the user to be audited. Select “Everyone” to audit anyone accessing the file or folder. Then click OK.
- Now back in the “Auditing entry” window, in the “Type” section, click on the dropdown button and select “All“. And in the “Basic permissions” section, check the “Full Control” option.
- Then click the OK button and also click all the OK buttons on each window that opens to apply them.
C. Viewing and Analyzing Logs.
- Open the “Event Viewer“. You can open it by clicking the Windows Start button and typing “event viewer” in the search box.
- In the Event Viewer Window, navigate to “Windows Logs > Security“.
- You’ll see the results of a Windows audit, including Audit Success and Audit Failure. Double click to see the details.
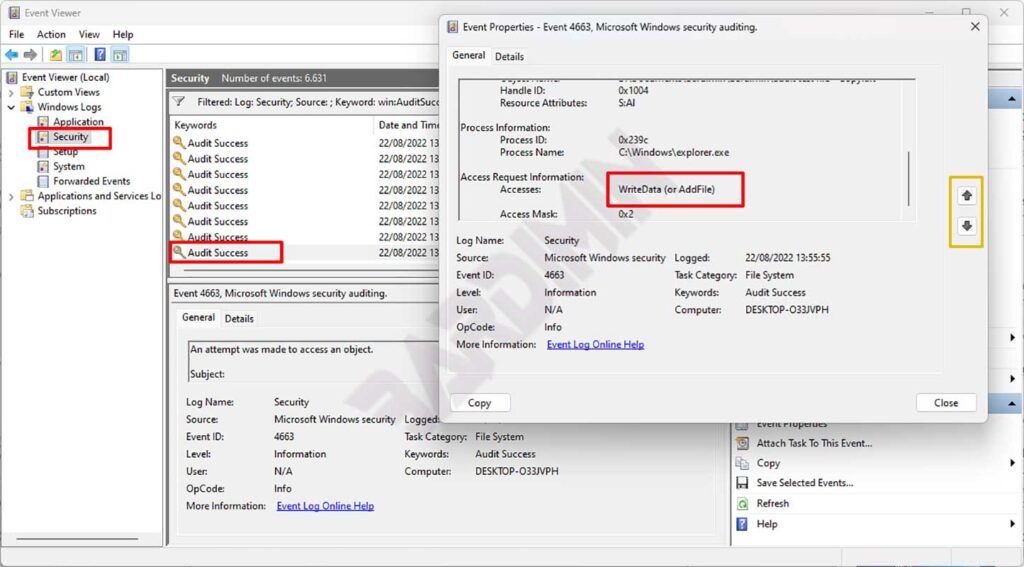
- Slide the arrow up or down to see more audit results.


