Memory Compression will improve the performance of RAM usage by compressing data so that RAM can hold more data.
Memory Compression is one of the features of Windows 11 to reduce data before it is written to RAM compressing the data.
This procedure allows the computer to store more files in physical memory than usual and reduces the amount of memory used per process. So the need for the operating system to use the paging file is getting smaller.
Compressing data in memory is much faster than the alternative of paging data to disk, and more efficient than using paging files. Compressed memory has no drawbacks and when Windows needs more memory, it will automatically compress the data in memory.
When you enable Memory Compression, the data compression process will use CPU resources. To reduce lag, it’s a good idea to use a high-end or up-to-date CPU.
How to See if Memory Compression is Enabled or Disabled
Check Memory Compression through Task Manager
- Open the “Task Manager” windows 11. You can open it by using the keyboard shortcut (CTRL + SHIFT + ESC).
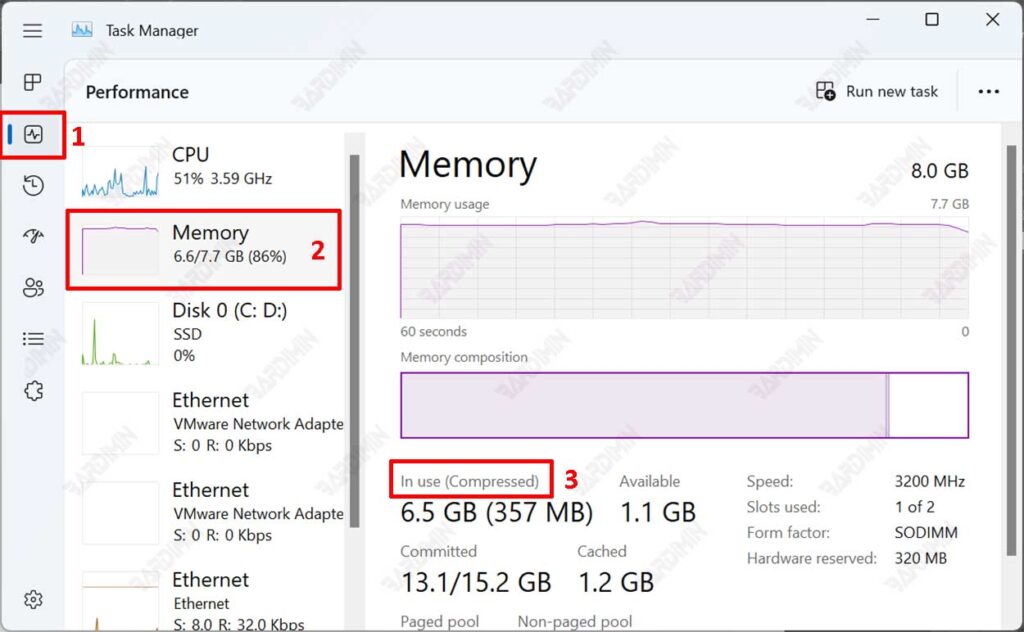
- Then navigate to “Performance >> Memory“.
- Next on the right pane, look at the memory usage status on “In use“. If it is “Compressed“, it means that Memory Compression is “Active“.
Check Memory Compression via PowerShell
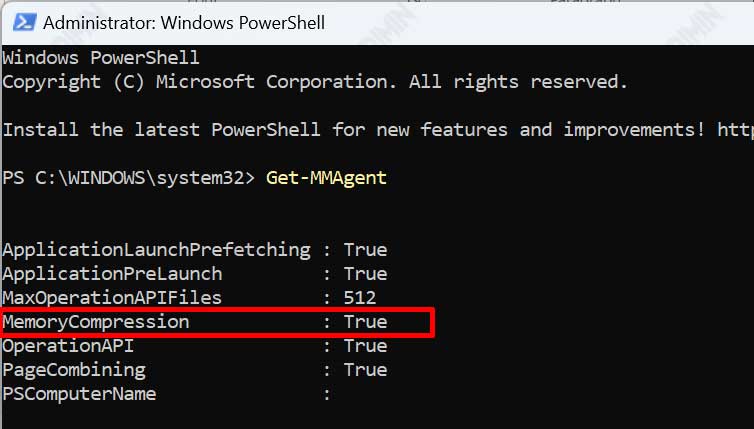
- Open “PowerShell” and run it as Administrator.
- Then type the following command
Get-MMAgent
How to Disable Memory Compression in Windows 11
- Open “PowerShell” and run it as Administrator.
- Then type the following command
Disable-MMAgent -mc
- Restart your computer.
How to Enable Memory Compression in Windows 11
- Open “PowerShell” and run it as Administrator.
- Then type the following command
Enable-MMAgent -mc
- Restart your computer.


