If you’ve tweaked every aspect of your Windows 11 computer and still aren’t getting high speeds, try disabling VBS. Disabling VBS has been shown to affect the speed of Windows 11. So, if you are a gamer and want to see if this improves the efficiency of the game, this article may be of interest.
Virtualization Based Security (VBS) in Windows 11 is a security feature that utilizes hardware virtualization technology to isolate the operating system and maintain its integrity. This feature provides an additional layer of security on top of the installed operating system and helps protect against firmware and kernel-based attacks.
In VBS, the installed operating system runs inside a virtual machine, called Virtual Secure Mode (VSM). VSM runs in an isolated mode that does not allow direct interaction with the operating system and applications. This feature can protect sensitive data and encryption keys, prevent attacks from rootkits and malware, and ensure that the operating system runs in a strong security environment.
VBS features in Windows 11
Some of the security features provided by VBS in Windows 11 include:
- Credential Guard: protects user credentials by storing them inside a VSM isolated from the operating system.
- Device Guard: ensures that only applications that have been verified and signed by Microsoft or an administrator can run.
- Windows Defender Application Guard: helps prevent attacks from malware and phishing on the browser by running the browser in an isolated virtual machine.
- Hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI): protects the kernel from alterations by malware and rootkits.
Impact of VBS on PC Performance
In general, the use of Virtualization Based Security (VBS) in Windows 11 does not have a significant negative effect. However, some factors to consider are:
- System performance: Because VBS runs isolated virtual machines to maintain security, this can add to the load on the system. Although VBS is designed to work efficiently, there may be a slight decrease in system performance in some cases.
- Hardware limitations: VBS requires adequate virtualization hardware support on the processor and chipset. If the hardware does not support virtualization technology or is not powerful enough, VBS may not be enabled.
- Application compatibility: VBS may not be compatible with some applications that use its own virtualization technology. Users should ensure that the applications they use will not be affected by VBS before enabling it.
- Complex settings: VBS settings require additional settings and more complex administration compared to standard security settings in Windows 11. Users unfamiliar with security configurations may need to learn more before enabling VBS.
Using Virtualization Based Security (VBS) in Windows 11 can affect gaming performance, especially if the game requires direct access to hardware such as a graphics card or requires higher kernel access.
VBS runs isolated virtual machines and restricts direct access to hardware, which can add overhead and slow down system performance. In some cases, this may result in decreased performance in the game and make it slower.
However, not all games will be affected by VBS. Some games may not require direct access to hardware or require lower kernel access. These games may still be able to run smoothly on systems with VBS enabled.
Although there are several factors to consider, the security benefits provided by VBS usually far outweigh the potential downsides. Therefore, many organizations and users are choosing to enable VBS in Windows 11 to enhance the security of their systems.
Checking VBS Status in Windows 11
You can use several ways to check the status of Virtualization Based Security (VBS) in Windows 11:
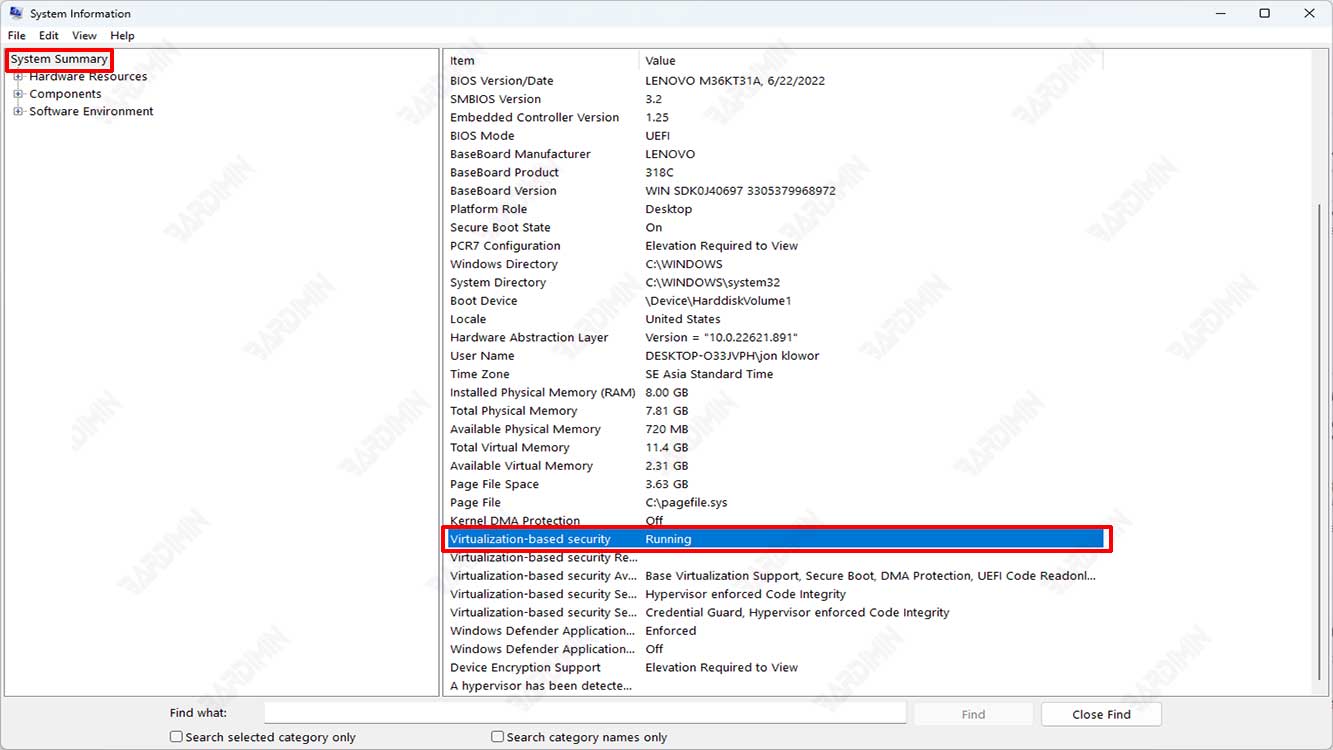
1. Through the System Information menu:
- Open the Start menu and type “System Information” in the search field, then click the System Information application that appears in the search results.
- In the System Information window, click on the System Summary category on the left side of the window.
- In the right part of the window, check that there is information “Virtualization-based security” and that the status is listed “Running” or “Not running”.
2. Via Command Prompt:
- Open Command Prompt by typing “cmd” in the Start search field, then right-click on the Command Prompt application and select “Run as administrator”.
- Type this command and press enter on the keyboard.
systeminfo
- Find the section “Virtualization-based security enabled” on the command output result. If the status is “Yes”, VBS has been enabled.
3. Via PowerShell:
- Open PowerShell by typing “PowerShell” in the Start search field, then right-click on the PowerShell application and select “Run as administrator”.
- Type the following command and press enter on the keyboard.
Get-CimInstance -ClassName <strong>“Win32_DeviceGuard”</strong> | Select-Object SecurityServicesRunning
- If the command output results show the value “CredentialGuard, DeviceGuard, VirtualSecureMode”, meaning VBS has been enabled
How to Disable VBS in Windows 11
Virtualization Based Security (VBS) can be disabled in Windows 11 through Windows security settings. Here are the steps to disable VBS in Windows 11:
- Open “Settings” by pressing the keyboard key (WIN + I) on the keyboard.
- Select “Privacy & Security > Windows Security”.
- On the right panel, click the button “Open Windows Security”.

- In the new window that opens, select “Device Security”.
- Then on the right panel, click the link “Core isolation details” in the “Core isolation”.
- Then in the “Memory integrity”, slide the switch button to the left to turn it off.

- After you turn it off, a warning message may appear that disabling VBS may affect system security, select “Yes” to continue.
- Restart your system to enable the changes.
How to Disable VBS in Windows 11 with Command Prompt
- Open Command Prompt by typing “cmd” in the Start search field, then right-click on the Command Prompt application and select “Run as administrator”.
- Type the following command and press enter on the keyboard.
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype off
How to Disable VBS in Windows 11 via Group Policy Editor
- Press the keyboard key (Win + R) and type “gpedit.msc”. Then click the OK button to open the Group Policy Editor.
- Then navigate to “Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Device Guard”.

- In the right pane, double-click “Turn On Virtualization Based Security”.
- Next in the dialog box, select “Disabled” to disable.
- Click the OK button to save the changes.
- Restart your computer.


