2. Find & Restart These 3 Critical Services:
a. Network Connections (NetMan)
Function: Manage a list of network connections (Wi-Fi/Ethernet/VPN) in the system.
Impact if problematic:
- The Network folder is empty or unresponsive.
- Can’t change the network adapter settings.
How to restart:
- Right-click Network Connections.
- Select Restart (if it’s running) or Start (if it’s status “Stopped”).
b. Network List Service (NetProfm)
Function: Detects and lists available networks (Wi-Fi/LAN).
Impact if problematic:
c. Network Location Awareness (NlaSvc)
Function: Identifies the type of network (Private/Public/Domain) and sets its security policies.
Impact if problematic:
- Windows misrecognizes the network (for example, it thinks of the home network as “Public”).
- Network Discovery doesn’t work, so other devices don’t appear.
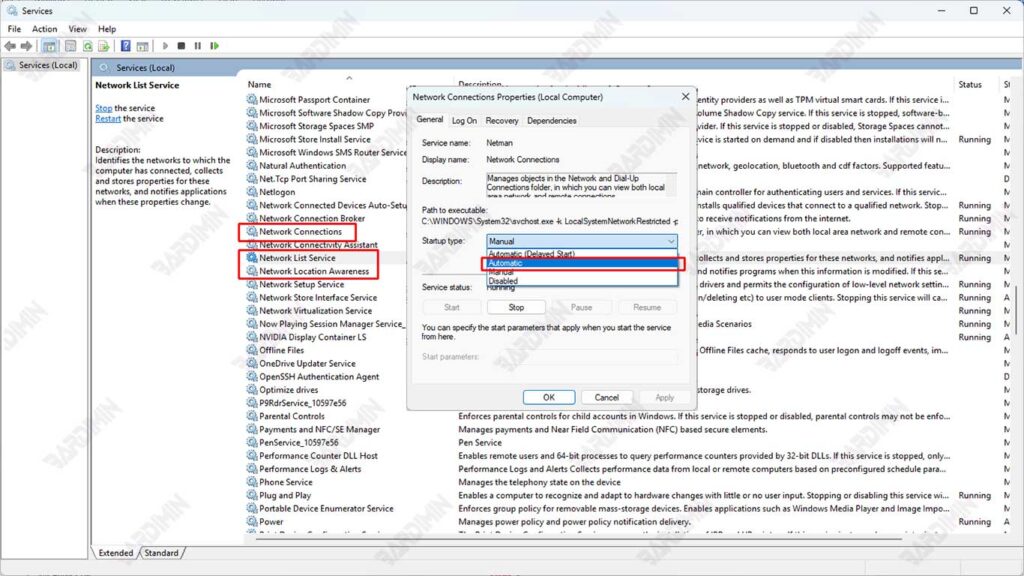
3. Set Startup Type to “Automatic”
To prevent the service from stopping again after a restart:
- Right-click on each > Properties service.
- In the General tab, change Startup type to Automatic.
- Click Apply > OK.
Solution 2: Fix Empty Network Folders with Command Prompt (Admin)
If restarting the network service hasn’t solved the problem, the next step is to run a series of CMD commands that can repair the Windows network configuration from the ground up. These commands work by:
- Clearing the DNS cache
- Reset the Windows network stack
- Update TCP/IP configuration
3 Essential Commands & Their Functions
1. netsh winsock reset
- Resets Winsock Catalog (a component that governs how programs communicate with the network).
- Fix errors such as:
- The network is connected, but can’t browse.
2. netcfg -d
- Deletes all network configurations and restores them to their default settings.
- Included:
- Remove corrupt network drivers.
- Reset all network adapters.
3. ipconfig /flushdns
- Clearing the Windows DNS cache.
- Fix the problem:
- The device does not appear in Network Explorer.
- Failed to access other computers via hostname.
How to Execute Commands Correctly
- Open CMD as Admin. Press Win + X → Select Terminal (Admin) or Command Prompt (Admin).
- Run Commands One by One
netsh winsock reset
netcfg -d
ipconfig /flushdns- Restart the computer. Changes only take effect after a restart.
Solution 3: Fix Empty Network Folder Issue via Registry Editor
If the previous solution has not worked, there may be a corruption in the Windows registry configuration that governs the network settings. The Registry is a central Windows database that stores all system settings, including information about network adapters, connections, and Network Explorer.
Registry Repair Steps
- Press Win + R, type regedit, and then press Enter.
- If you’re prompted for admin permission, click Yes.
2. Navigate to Problematic Key
- Enter the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Network
- Here, you’ll see several subkeys, including Config.
3. Rename or Remove Key “Config”
- Right-click on the key Config.
- Select Rename and rename it to Config_Old (for automatic backup).
- Or select Delete if you’re sure you want to delete it (Windows will create a new one on reboot).
4. Restart the Computer
After restarting, Windows will automatically recreate the key Config with the default settings.
By following this step, 90% of Network folders that are empty due to registry corruption can be repaired!
Solution 4: Create a New User Account to Isolate the Issue
When all previous solutions fail to fix an empty Network Folder in Windows 11, the problem may not lie with the system, but rather with the corrupt user profile. By creating a new account, we can determine whether:
- The problem only occurs in the old account (meaning the damage is in the user’s profile)
- Problems persist in new accounts (indication of deeper system corruption)

