Windows Services are programs that run in the background of the Windows operating system and provide important functions such as security, networking, printing, etc. Windows services can be started automatically when the system is turned on, or manually by the user or administrator. Windows services can also be stopped, paused, or resumed as needed.
One way to manage Windows services is to use Command Prompt or CMD. CMD is a built-in Windows tool that allows users to run text commands to perform various tasks. Using CMD, users can view a list of available Windows services, find out the status of the service, change the service’s startup mode, and control service operations such as starting, stopping, pausing, and resuming.
In this article, Bardimin will discuss how to manage Windows services using CMD with details and examples. This article will be divided into several parts, namely:
- How do I open CMD as an administrator
- How to view a list of available Windows services
- How to find out the status of Windows services
- How to change the startup mode of a Windows service
- How to control the operation of Windows services
How do I open CMD as an administrator
To manage Windows services using CMD, we need to open CMD as administrator. This is because some Windows services require high permissions to be changed or controlled. If we open CMD as a regular user, we might get error messages like “Access is denied” or “The requested pause, continue, or stop is not valid for this service”.
Here are the steps to open CMD as an administrator:
- Click the Start button in the lower-left corner of the screen
- Type cmd in the search box
- Right-click on the search result Command Prompt and select Run as administrator
- Click Yes on the User Account Control dialog box that appears
After that, we will see a CMD window with the title Administrator: Command Prompt. This signifies that we have successfully opened CMD as an administrator.
How to view a list of available Windows services
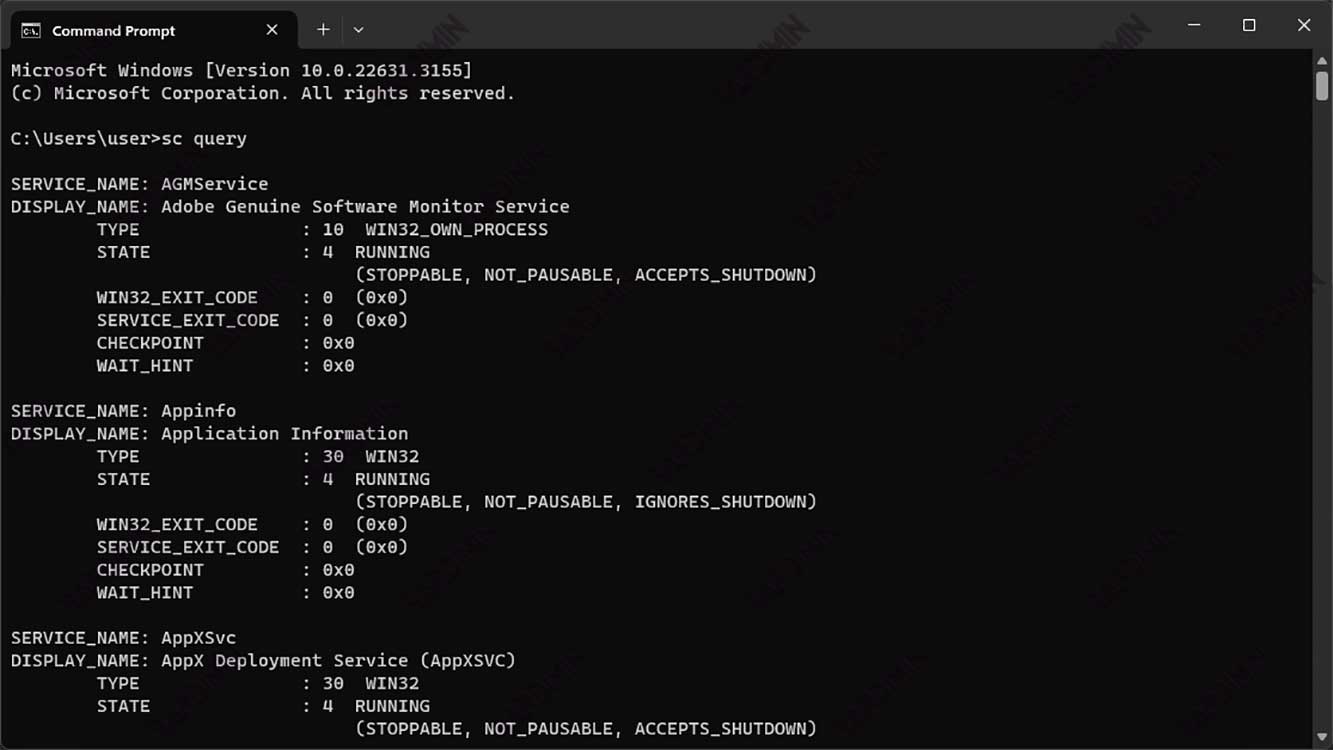
To see the list of Windows services available on our system, we can use the command sc query. This command will display information about all services registered in Windows, including the service name, display name, type, status, and others.
Here is an example output of the sc query command:
C:\Windows\system32>sc query
SERVICE_NAME: AdobeARMservice
DISPLAY_NAME: Adobe Acrobat Update Service
TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS
STATE : 4 RUNNING
(STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, ACCEPTS_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x0
...From the output above, we can see that there is some information displayed for each service, namely:
- SERVICE_NAME: This is the internal service name used by the system. This name is unique and cannot be changed. This name is also used as a parameter for other commands related to service.
- DISPLAY_NAME: This is the name displayed for the service in the user interface, such as Services or Task Manager. This name can be changed by the user or administrator through the service property.
- TYPE: This is the type of service, which determines how the service is run by the system. There are several types of services, namely:
- WIN32_OWN_PROCESS: This service runs in its process, which means it doesn’t share resources with other services. This service can interact with the user’s desktop if allowed.
- WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS: This service is run in a process along with other services of the same type. This service cannot interact with the user’s desktop.
- KERNEL_DRIVER: This service is a kernel device driver, which is part of the core operating system. This service runs when the system is turned on and cannot be stopped or paused by the user or administrator.
- FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER: This service is a file system driver, which manages access to the file system. This service runs when the system is turned on and cannot be stopped or paused by the user or administrator.
- STATE: This is the status of the service, which indicates the operational condition of the service. There are several service statuses, namely:
- STOPPED: This service is not running and doing nothing.
- START_PENDING: This service is in the process of starting, but not ready to accept requests yet.
- STOP_PENDING: This service is in the process of retiring, but has not completely stopped.
- RUNNING: This service is running and ready to accept requests.
- CONTINUE_PENDING: This service is in the process of resuming after being paused, but is not yet fully operational.
- PAUSE_PENDING: This service is in the process of pausing, but has not been completely paused.
- PAUSED: This service is paused and doesn’t accept new requests, but still retains its previous state and resources.
- WIN32_EXIT_CODE: This is the error code returned by the service when the service stops normally. If the service stops successfully, this code will be 0. If the service stops with an error, this code will indicate the type of error that occurred. This code can be searched on the internet to get further explanation.
- SERVICE_EXIT_CODE: This is the error code returned by the service when the service stops for a specific reason specified by the service itself. If the service does not specify a specific reason, this code will be 0. This code can be searched on the internet to get further explanation.
- CHECKPOINT: This is the value used by the system to monitor the progress of the service while the service is in the process of starting, stopping, pausing, or resuming. This value will increment periodically during the process and will reset to 0 when the process is complete. If this value does not change within the time specified by the WAIT_HINT, the system assumes that the service has failed.
- WAIT_HINT: This is the maximum time in milliseconds estimated by the service to complete the start, stop, pause, or resume process.

