Windows Defender has a Ransomware protection option which is disabled by default.
Ransomware is a type of malware that threatens its victims to publish private data or block access to data files by encrypting the files by demanding a ransom to restore them.
Some simple ransomware variants can lock the system without damaging any files and more sophisticated ones use a technique called cryptoviral extortion. This ransomware will encrypt the victim’s files so that they are inaccessible and demand a ransom payment to decrypt the files.
There is no guarantee that if you pay the ransom, you will get the unlock key to regaining access to the files that the ransomware encrypted.
The Ransomware protection option has been around for a long time in Windows Defender, but this option is disabled by default.
Maybe you are wondering why this option is disabled by default? Quite some third-party anti-ransomware programs exist and experience false positives. This issue may cause the ransomware protection option in Windows Defender not being active by default.
One of the most effective ways to prevent Ransomware is to be careful how you use your computer, especially when you are connected to the internet. Then you can also do it by always making a backup of the important files that you create.
Activating Ransomware Protection
Ransomware Protection Windows Defender works by blocking all access to files, folders, and memory. Applications can only make changes that you have permitted to make changes.
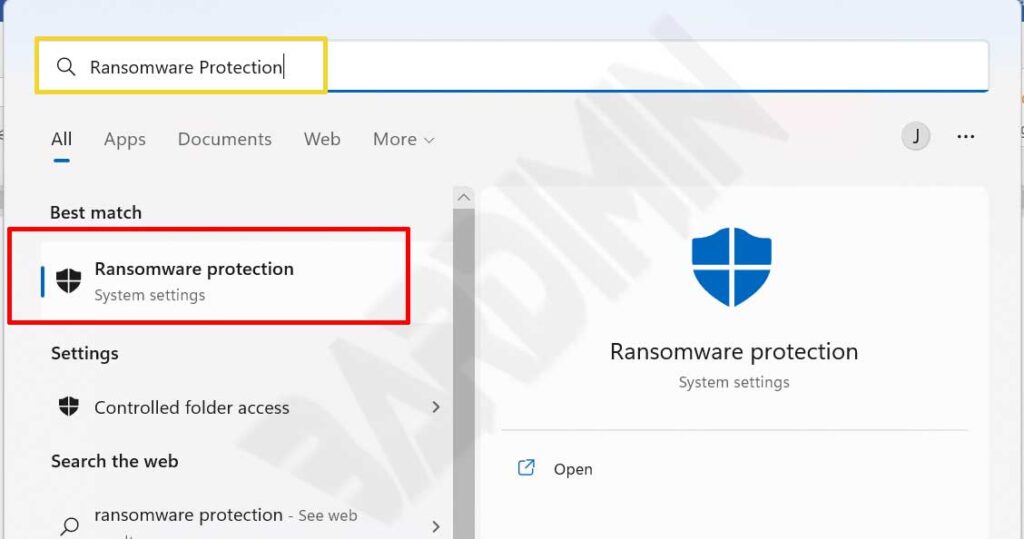
- Open ” Ransomware Protection ” by typing “ransomware protection” in the Windows search menu.
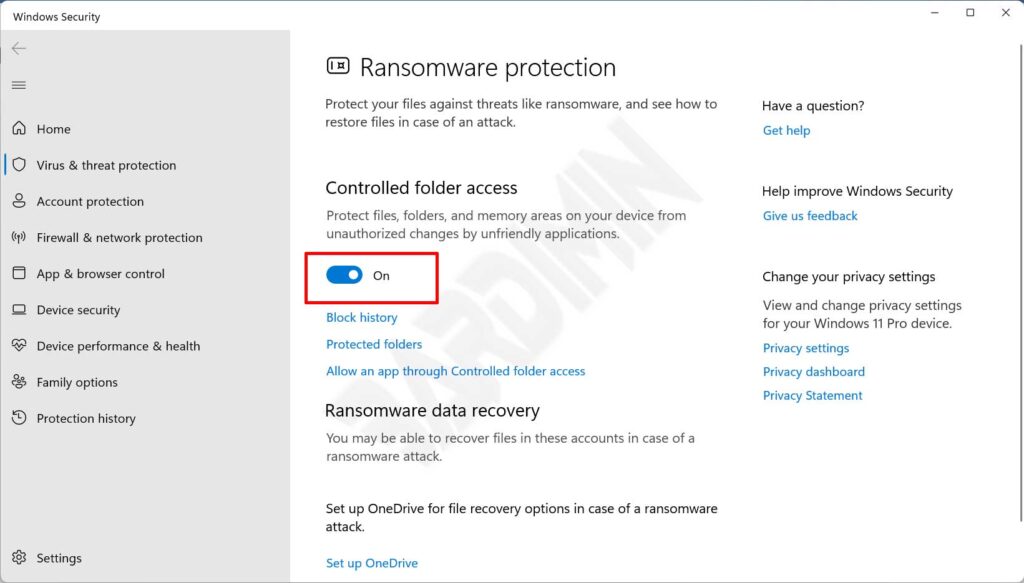
- Then in ” Controlled folder access ” slide the switch to the right to activate.
Set app permissions on Ransomware Protection
After you activate Ransomware Protection as in the previous method, protected files or folders will not be accessible to other applications, including Word and Excel.
To give the application for permission to access the file folder, you can do it by:
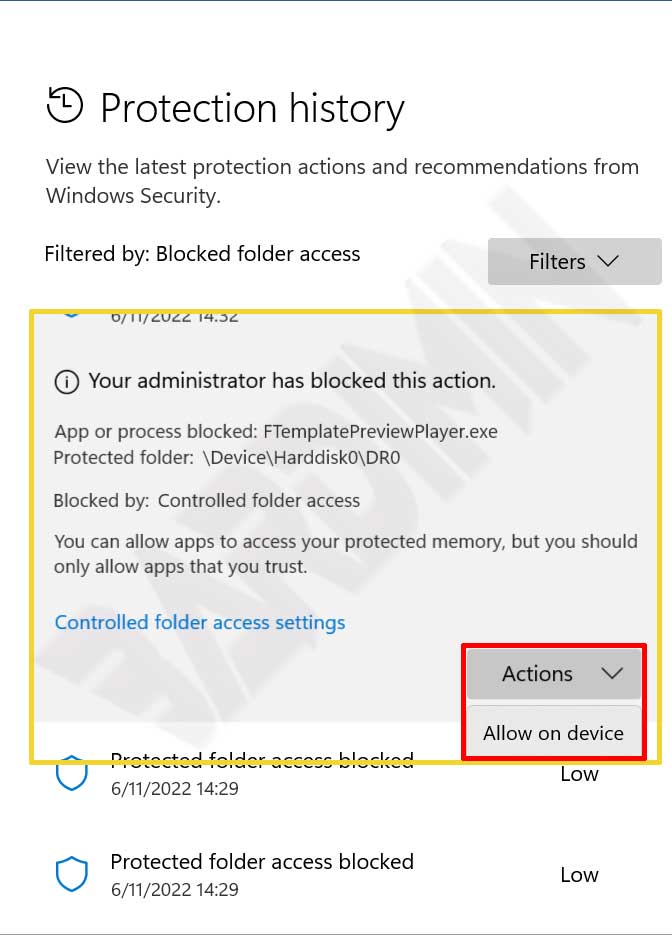
Block History
- Click the “ Block History ” button
- Select it and click the history list to expand.
- Click the “ Actions ” button and select “ Allow on device ”
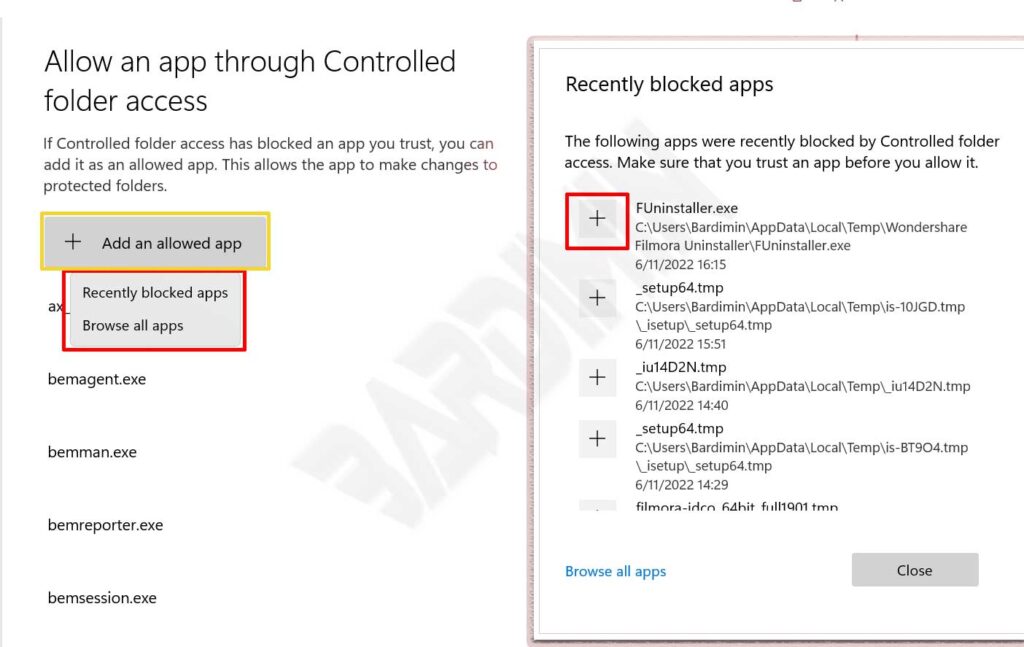
Allow an app through Controlled folder access
- Click the “ Allow an app through Controlled folder access ” button
- Click ” Add an allowed app “
- There are two options that you can choose, namely ” Recently blocked apps ” and ” Browse all apps “
- If you want to add permission from the list of blocked apps, select “ Recently blocked apps”. Then click the plus (+) button to give the application for permission.
- And if you want to add other applications, select ” Browse all apps”. Then navigate to the exe file of the application you want to give permission.