Have you ever been frustrated searching for one important file in the middle of thousands of documents in Windows 11, when you remember exactly what the text is in it, but forgot the name of the file? This problem often haunts Windows users, from students to professionals.
Windows 11’s built-in search feature often fails to find files based on text content, especially for formats like PDF, Excel, or encrypted documents. As a result, many people spend hours opening folders one by one when there are smarter ways to get them done in a matter of seconds!
Finding files based on text content opens up new opportunities in data management, legal document tracking, digital evidence collection, and administrative archiving. However, to make effective use of this feature, it takes an in-depth understanding of how Windows Search Indexing works and the proper use of search syntax.
The Standard Way to Search for Files Containing Specific Text
Windows 11 has been equipped with a search feature that is capable enough to search for files based on the content or content of text within them. This feature is especially useful when you don’t remember the specific name of the file, but you still remember the body or keyword part of the document. With a little understanding of search syntax and built-in feature optimization, you can find files quickly and efficiently, without the need to rely on additional software.
1. Use the Search Feature in File Explorer
One of the most straightforward ways to search for files based on text content is to use the Search feature within File Explorer. This method is perfect for basic search needs, especially if you know the location of the folder where the files are most likely to be stored.
Steps:
- Press the Win + E button to open the File Explorer.
- Point to the target folder, such as D:Documents or another folder where your files are stored.
- In the upper-right corner of the File Explorer window, type a search query using the format:
content:”text to search for”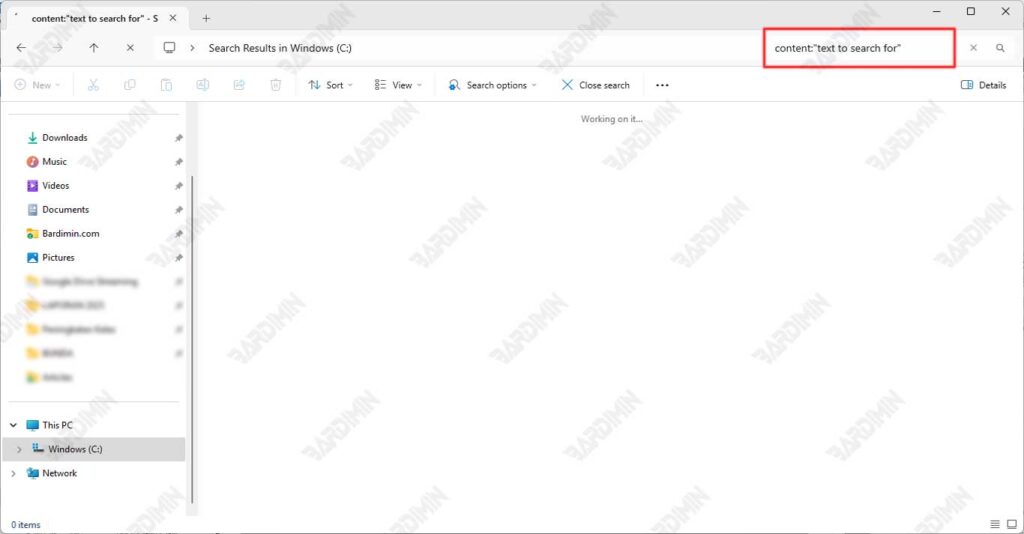
2. Use Advanced Search Operator in Windows 11
If you want to improve search accuracy and narrow down search results in Windows 11, using the advanced search operator (Advanced Query Syntax/AQS) is the best solution. This operator allows you to structure more complex and focused search queries, so the system only displays files that match your criteria.
List of Windows 11 Advanced Search Operators
a. Search Based on File Content
The content:”searched text” operator is a powerful weapon when you only remember part of the contents of a document but forget the name of the file. This feature works by scanning the actual content inside the file, not just metadata or file names.
Example:
- content:”cooperation agreement” will find all the files that contain the phrase in the text
- Supports popular formats such as DOCX, PDF, TXT, and even some database formats
b. Filter by File Type
The ext:[extension] operator allows you to filter search results based on specific file formats. This is especially useful when you just want to search for a specific type of document.
Example:
- ext:pdf to find all PDF documents
- ext:xlsx special Excel file
- Can be combined with other operators for more specific searches
c. Search by Modification Time
modified:[time] helps you track files based on the last time they were modified. This feature is worth looking for:
- modified:today for recently edited documents
- modified:lastmonth to find the old version of the
- Ideal for tracking the latest version of documents or recovering accidentally altered files
d. Filtering by File Size
The size:[size] operator allows you to sort files by their size.
Example:
- size:>50MB to find large files that may take up storage space
- size:<500KB for small text documents
- Helps in disk storage management and cleanup
Operator Combinations: Super Effective Strategies for Precision Search
Mastering one search operator is beneficial, but combining multiple operators at once will take you to the next level in file search in Windows 11. This combination allows you to filter files more specifically, accurately, and efficiently, especially if you’re working with thousands of files in different formats and locations.
1. Find a Word document that contains the word “proposal” and was changed this month
kind:=document content:”proposal” modified:thismonthExplanation:
- kind:=document limit the search to only documents (Word, PDF, etc).
- content:”proposal” search for a file that contains the word “proposal” in its contents.
- modified:thismonth ensures that the file has been changed within the current month.
2. Find a PDF file about “profit and loss report” in a specific folder
content:”profit and loss report” ext:pdfExplanation:
- content:”profit and loss report” searches for the contents of the file that contains the phrase.
- ext:pdf filters only files with PDF extensions.
3. Look for the text file (.txt) containing the “password” created last week
content:”password” ext:txt modified:lastweekExplanation:
- content:”password” search for files that contain the word “password”.
- ext:txt filters only text files (.txt).
- modified:lastweek focuses the results on files that were modified during the past week.
✔ Use the = sign for exact searches (example: kind:=document).
✔ Use a wildcard * for a partial search (example: filename:*report*).
Power User Technique: Deeper and Super Fast Search
For those of you who want high-performance, maximum accuracy, and are not satisfied with just the built-in features of Windows Explorer, then this Power User technique is a must-master. By utilizing PowerShell and Command Prompt (CMD), you can perform a search, file by content, much faster, more efficiently, and more accurately especially when working with thousands of files in many subfolders.
1. Take Advantage of PowerShell – Faster than File Explorer!
PowerShell is an advanced automation tool available on Windows, and it has the incredible ability to perform text searches within files recursively (including subfolders).
Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\TargetFolder” -Recurse | Select-String -Pattern “keywords”Explanation:
- Get-ChildItem works to browse files and folders.
- -Recurse ensures that searches are also performed across all subfolders.
- Select-String -Pattern scans the contents of the file and looks for a match to the word or phrase you specify.
Key advantages of PowerShell:
- It can process thousands of files in just a matter of seconds.
- Supports regular expression-based (regex) search for more flexible results.
- Can be combined with automation and logging scripts.
2. Use the findstr Command in CMD for Bulk Search
If you are more comfortable using Command Prompt (CMD), then the findstr command is a lightweight and fast option for searching text in files in bulk, especially text files and lightweight documents.
findstr /s /i /m “secret text” *.docxParameter explanation:
- /s = Search in all subfolders recursively.
- /i = Ignores case-insensitive differences.
- /m = Displays only the name of the file that contains text (without displaying the contents of the file).


