Implementing custom functions as structured components is an essential practice in Yii2 application development. This technical guide provides a systematic approach to creating globally accessible functions in Controllers and Views, with detailed explanations for both Yii2 Basic and Advanced templates.
In Yii2-based software engineering, functions are fundamental components that encapsulate business logic into separate, reusable units. This approach not only reduces code duplication but also enhances readability. Professional developers often face challenges in organizing helper functions for global access without compromising the framework architecture.
An elegant solution involves implementing these functions as official Yii2 components. This method aligns with the Don’t Repeat Yourself (DRY) principle and Yii’s dependency injection conventions. This article guides you through a systematic technical process for creating Yii2 custom functions.
Core Concepts of Function Components in Yii2
Before technical implementation, understand Yii2’s component philosophy. This framework features a component-based architecture that separates application functions into independent units. Each component is a class instance registered within Yii::$app.
The primary advantages include centralized configuration and simplified testing. Additionally, you can organize namespaces precisely according to project structure. Therefore, converting regular functions into Yii2 components represents a long-term investment for code maintainability.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
The Yii2 component creation process follows a structured workflow. Differences between Basic and Advanced templates involve file placement and namespace configuration.
- Create Component Directory Structure
Create a folder namedcomponentsin the appropriate location. For Yii2 Basic Template, place this folder in the application root. For Yii2 Advanced Template, create it inside thecommondirectory.
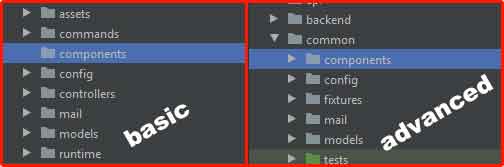
- Design Your Function Component Class
Create a new PHP file in the components folder, for exampleAppFunction.php. This class must extendyii\base\Component.
<?php
// Namespace for Yii2 Advanced Template
namespace common\components;
// Namespace for Yii2 Basic Template
// namespace app\components;
use yii\base\Component;
class AppFunction extends Component
{
/**
* Example function for demonstration
* @param string $name User name parameter
* @return string Formatted greeting message
*/
public function generateGreeting($name = 'Developer')
{
// Input validation for security
$name = htmlspecialchars(trim($name), ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
// Business logic can be added here
return "Welcome, {$name}!";
}
/**
* Example utility function
* @param float $amount Value to format
* @return string Currency-formatted number
*/
public function formatCurrency($amount)
{
return '$' . number_format($amount, 2, '.', ',');
}
}Notice the use of docblock comments explaining each function’s purpose. This practice is recommended for proper code documentation. Additionally, always implement input sanitization to prevent XSS vulnerabilities.
- Configure Component in Configuration Files
Components must be registered in the application configuration to be accessible via Yii::$app. This process differs between the two templates.
For Yii2 Advanced Template: Edit common/config/main.php:
'components' => [
// Default Yii2 component configuration
'db' => [ ... ],
'cache' => [ ... ],
// Your custom component
'appFunction' => [
'class' => 'common\components\AppFunction',
],
],For Yii2 Basic Template: Edit config/web.php:
'components' => [
// ... existing configuration
'appFunction' => [
'class' => 'app\components\AppFunction',
],
],Component naming uses camelCase following Yii2 conventions. This name becomes the key for accessing the component throughout your application.
- Implementation and Function Calls
After configuration, the component becomes callable from various application parts.
// 1. Calling from Controller
namespace frontend\controllers;
use Yii;
use yii\web\Controller;
class SiteController extends Controller
{
public function actionIndex()
{
// Using generateGreeting function
$message = Yii::$app->appFunction->generateGreeting('John');
// Using formatCurrency function
$price = Yii::$app->appFunction->formatCurrency(1500.00);
return $this->render('index', [
'message' => $message,
'price' => $price,
]);
}
}
// 2. Direct View call
<div class="welcome-message">
<?= Yii::$app->appFunction->generateGreeting($user->name) ?>
</div>
// 3. Model integration
class Product extends \yii\db\ActiveRecord
{
public function getFormattedPrice()
{
return Yii::$app->appFunction->formatCurrency($this->price);
}
}Best Practices and Optimization
To ensure optimal Yii2 function implementation, consider these guidelines:
- Single Responsibility Principle: Each function should handle one specific task
- Error Handling: Implement try-catch mechanisms for critical operations
- Performance Consideration: Apply caching for resource-intensive functions
- Type Hinting: Use parameter and return type declarations
- Unit Testing: Create test cases for every function
Advanced implementation example with error handling:
public function processData(array $data)
{
try {
if (empty($data)) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('Data cannot be empty');
}
// Processing logic
$result = array_map(function($item) {
return $this->transformItem($item);
}, $data);
return $result;
} catch (\Exception $e) {
Yii::error("Error processing data: " . $e->getMessage());
return [];
}
}Common Problem Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Class not found | Incorrect namespace | Run composer dump-autoload |
| Component not registered | Configuration error | Verify ‘components’ array |
| Function undefined | Non-public method | Check method visibility |
| Performance issues | Repeated function calls | Implement caching |
For comprehensive component architecture details, visit the official Yii 2.0 Components documentation.
Conclusion
Creating functions as structured components in Yii2 represents essential expertise for professional developers. This approach provides technical solutions for function accessibility challenges. By following this systematic guide, you can build more organized and secure codebases.
Proper implementation significantly impacts application maintainability. Additionally, always consider thorough documentation and testing for each function. Consequently, your Yii2 application development will become more efficient and professional.


