Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) is a software-based storage solution from Microsoft designed specifically for hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) environments. By leveraging local drives across multiple servers, S2D enables businesses to build distributed, scalable, and cost-effective storage systems.
One of S2D’s main advantages is its ability to improve storage efficiency and server performance. With features such as SSD caching, S2D uses SSDs as a cache to speed up data access, so applications that require high speeds, such as databases and virtualization, can run more optimally.
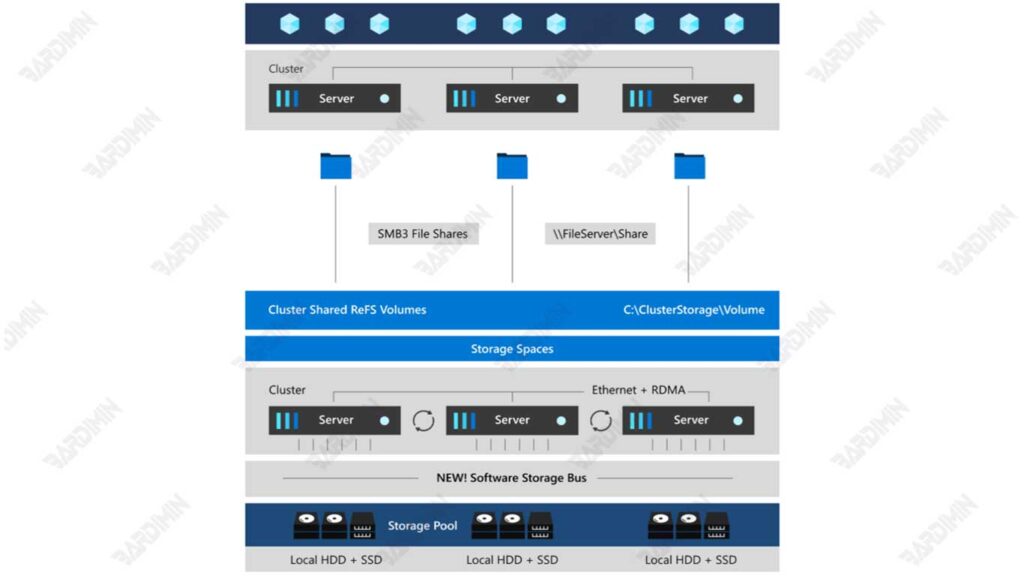
In addition, S2D provides resiliency options such as mirroring (two or three copies of data) and parity (similar to RAID 5/6) that ensure data remains safe even in the event of a hardware failure. S2D integration with Windows Server technologies such as Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) and ReFS also makes data management easier, while support for Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) ensures low latency in high-speed networks.
S2D has advantages over RAID, making it more suitable for today’s business needs. RAID is limited in flexibility and expandability. S2D allows the use of local drives across multiple servers, flexible addition of servers and drives, and offers more secure three-way mirroring than RAID 1 or RAID 5.
S2D also integrates with Windows Server, making it easy to manage through PowerShell or Windows Admin Center, and reducing the need for investment in dedicated storage systems such as SAN/NAS. With all these advantages, S2D is a modern and cost-effective option for a reliable storage solution.
What is Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)?
Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) is a software-defined storage technology (SDS) introduced by Microsoft in Windows Server. The technology is designed to manage cluster-based storage by combining multiple local storage devices from multiple servers into a single distributed storage pool. With S2D, organizations can build storage infrastructure that is extensible, highly available, and cost-efficient without the need to use external storage devices such as SAN (Storage Area Network) or NAS (Network Attached Storage).
S2D works by automating storage management through disk-tiering, caching, and mirroring/parity technologies to improve access speed and capacity efficiency. By utilizing various types of storage media such as NVMe, SSD, and HDD, S2D can deliver high performance while maintaining data redundancy to prevent system failure.
History and Development of S2D Technology in Windows Server
The Storage Spaces technology was first launched in Windows Server 2012 as a feature to manage storage pools more flexibly. However, at that time, this feature still requires JBOD (Just a Bunch of Disks) and can’t support distributed storage in clusters.
In Windows Server 2016, Microsoft introduced Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) as a more advanced storage solution, supporting (HCI) hyper-converged infrastructure. This technology allows the consolidation of internal storage from multiple servers into a single storage cluster without the need for a SAN or NAS.
Furthermore, in Windows Server 2019, S2D has been enhanced with performance improvements and features, such as:
- Cluster Performance History – Monitor storage performance in real-time.
- Mirror-Accelerated Parity – A combination of mirror and parity modes to achieve a balance between performance and capacity.
- Scalability up to 16 nodes – Allows for greater expansion than previous versions.
Until the latest version of Windows Server 2022, S2D has been further optimized with support for higher performance, better storage efficiency, and stronger data security.

