Permission management in the operating system, especially in Windows 11, is a crucial aspect that directly impacts user security and productivity. The following explains the importance of permit management and its impact.
Permission management functions to manage user access to disks, folders, and files. Each object in the system has permissions that determine who can access it and what can be done with it.
With proper permission management, administrators can ensure that only authorized users can access or modify sensitive data. This is essential for preventing unauthorized access and protecting important information from potential leaks or damage.
What Are Disk, Folder, and File Permissions?
Managing disk, folder, and file permissions is an important aspect of the Windows 11 operating system that manages user access to various objects in the system. These permissions specify who can perform certain actions on the object, such as reading, writing, or erasing.
Permissions are rules that are set to control access to objects within the operating system, such as disks, folders, and files. Each object has permissions that govern what a specific user or group of users can do. The role of permissions in an operating system is very important because:
- Security: Permissions help protect data from unauthorized access, so only authorized users can access sensitive information.
- Access Control: Administrators can manage who has access to specific objects, giving them greater control over system resources.
- Data Integrity: By establishing the right permissions, the risk of deletion or modification of important data can be minimized.
Types of Permissions in Windows 11
Permission management in Windows 11 is essential for controlling user access to disks, folders, and files. The following is an explanation of the types of permits that are commonly used:
1. Full Control
Allows users to create, read, modify, and delete folders and subfolder contents. Users can also run applications from those objects.
Usage Examples: Administrators who manage system folders, allowing them to organize all aspects of folders and their contents.
2. Modify
Allows users to create and read the contents of folders, as well as modify content. However, this permission does not allow users to delete subfolders.
Usage Example: Ordinary users who need to edit documents without the risk of deleting important files.
3. Read and Execute
Allows access to the contents of folders and runs the applications that are in them.
Usage Example: A user who only needs to run the application without changing the file, such as a user running a software program.
4. List Folder Contents
Allows users to view the contents of folders without granting further access to the files inside.
Usage Example: A user who needs to check the files in a folder without editing or deleting them.
5. Read
Allows access to the contents of the file without running the application. Users can view the contents of the file, but cannot change it.
Usage Example: A user who only needs to read a document, such as reading a report or article.
6. Write
Allows users to add files and subfolders to folders, but not to delete existing files.
Usage Example: A user who needs to save a new document, such as an author who saves a draft of their work.
Manage permissions in Windows 11
Managing disk, folder, and file permissions in Windows 11 is essential for maintaining data security and integrity. Here’s an explanation of how to view, change, and set advanced permissions:
How to View and Change Permissions
Steps to access the permissions menu via Properties:
- Right-click on the disk, folder, or file you want to set permissions for
- Select “Properties” from the context menu
- Click the “Security” tab in the Properties window
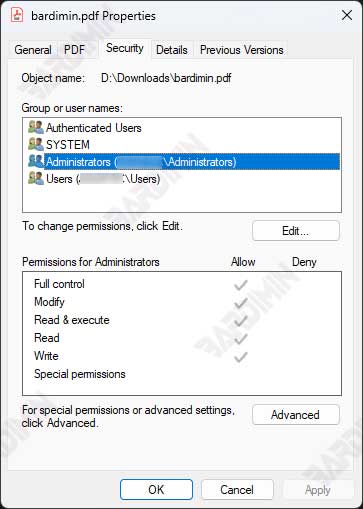
Explanation of the Security tab and the available options:
- The Security tab displays the groups of users who have permissions on the selected object
- You can select a user group to check what permissions they have
- The “Edit” button allows you to change permissions for selected user groups
Editing Permissions for Users
To add or remove permissions for a user group:
- Select the user group whose permissions you want to change
- Click the “Edit” button
- In the Edit window, you can choose to add or remove permissions
- Click “Apply” to assign a new permission
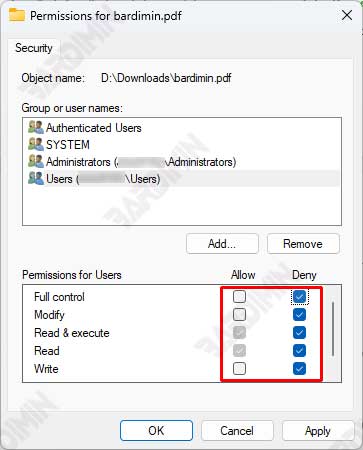
The importance of ensuring users have the right permissions:
- Grant permissions according to the user’s needs, no more or less
- The right permissions will increase productivity and minimize security risks
Advanced Permission Settings
Explanation of the Advanced option and its use:
- Click the “Advanced” button on the Security tab to access advanced settings
- Advanced Security Settings window provides more granular control
- You can set permissions for the current folder, subfolders, or files only
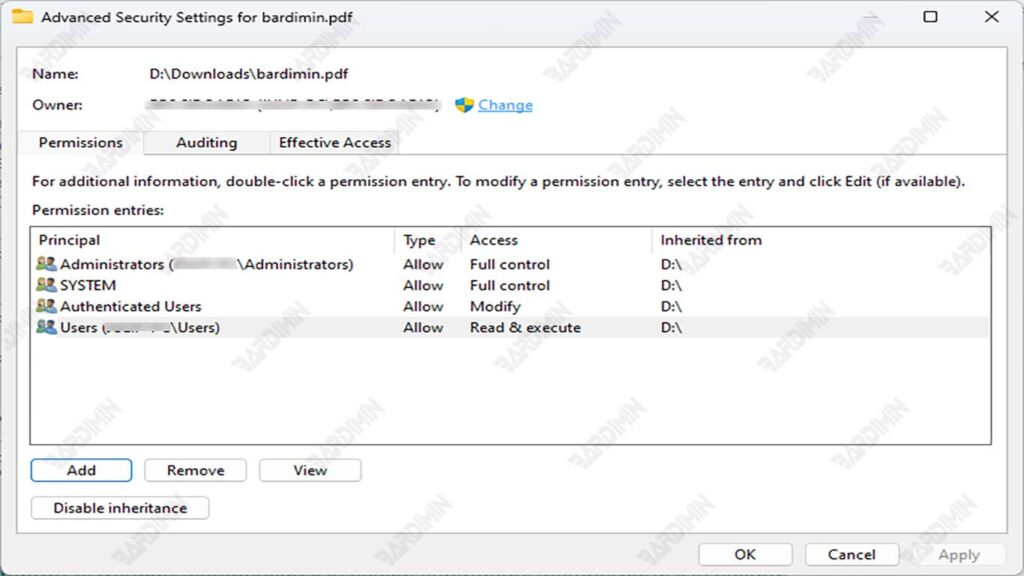
Examples of situations where advanced permissions are required:
- When it is necessary to set permissions more specifically, such as only for certain files
- When you need tighter control over access to resources
Common Mistakes in Permit Management
While permission management in Windows 11 is very important, there are some common mistakes that users often make. Here is a discussion about these mistakes along with tips to overcome them:
Granting Permission That Is Too Loose
- Error: Excessively granting Full Control permissions to users who don’t need them.
- Impact: Increases security risk if a user’s account is misused.
- Tip: Grant permissions based on the user’s minimum needs, such as Modify or Read. Avoid granting Full Control permissions unless necessary.
Not Renewing Permissions
- Error: Didn’t change permissions when a user switched tasks or left the organization.
- Impact: Users can continue to access data even if they no longer need it.
- Tip: Regularly check and update user permissions as needed. Remove permissions for users who are no longer active.
Setting Permissions at the Wrong Level
- Error: Assigning permissions at the wrong level, such as setting permissions on the root disk.
- Impact: This may cause problems with the operating system if permissions are incorrect.
- Tip: Set permissions to the lowest possible level, such as on individual folders or files. Avoid setting permissions at the disk or volume level.
Not Understanding Permission Inheritance
- Error: Doesn’t understand the concept of permission inheritance from folders to subfolders and files.
- Impact: Inconsistent permissions can cause access issues.
- Tip: Understand the concept of permission inheritance and use advanced settings if necessary to set permissions specifically.
Conclusion
Proper permission management is essential for maintaining data security and integrity in Windows 11. By granting permissions as needed, updating permissions regularly, and understanding the concept of permission inheritance, you can avoid common mistakes in managing permissions. Implement best practices in permission management to ensure your systems are secure and productive.


