DNS over HTTPS (DoH), also known as “DNS encryption” in Windows, is a method for encrypting DNS queries and responses between a user’s computer and a DNS server.
When you connect to a Web site or other Internet host, your computer must first query a Domain Name System (DNS) server for the IP address associated with the hostname.
DNS, also known as the “Internet phone book”, is a critical part of the infrastructure required to provide consumers with an optimal online experience. Almost every online activity, from browsing websites to using services through mobile apps to checking and sending emails, starts with the client looking up the IP address of the service using the Domain Name System.

When you access a website using a domain name (for example, “google.com”), your computer sends a request to a Domain Name System (DNS) server. The DNS server uses the domain name to look up the corresponding IP address in a list. It returns the IP address to your computer, which you then use to access the site.
This domain name lookup process usually happens over an unencrypted network. Any point on the path between you and the site you’re viewing can intercept the domain name. If you’ve been paying attention to the current security environment, you may have heard of DNS over HTTPS, also known as DoH.
DNS over HTTPS encrypts the interaction between your computer and DoH-enabled DNS servers. DoH allows your computer to perform these DNS lookups over a secure HTTPS connection instead of over plain text DNS lookups that can be intercepted by ISPs and governments. No one can intercept your DNS requests and spy on the sites you visit or tamper with the DNS server responses.
What is DNS over HTTPS (DoH)
DNS over HTTPS (DoH) is a protocol that allows clients (such as web browsers) to encrypt DNS (Domain Name System) requests to DNS servers by using the more secure HTTPS protocol.
As an alternative to regular DNS which uses the unencrypted UDP protocol, DoH allows users to obtain higher security and privacy as the transmitted DNS data is invisible to third parties trying to snoop or steal user information.
DNS over HTTPS is not the same as DNS over TLS (DoT). While they both encrypt, they differ in one important way: the port they use. DoT uses a specific port, 853, while DoH uses port 433.
Even though the DoT is encrypted, administrators monitoring the network can see the requests coming and going as it uses a dedicated port, although it will be difficult to see the information due to the encryption.
DoH, on the other hand, uses the same port as all other HTTPS communications, such as web browsing. It is hidden among the large amount of HTTPS data flowing in and out of the network. And this is good for privacy because it makes it difficult for network administrators to maintain visibility. However, it can be detrimental to network administrators because it makes it more difficult to prevent malicious DNS requests.
Free DNS Server List
The following is the list of free IPv4 DNS service addresses:
- Google DNS Primer: 8.8.8.8
- Google Secondary DNS: 8.8.4.4
- Cloudflare DNS Primer: 1.1.1.1
- Cloudflare Secondary DNS: 1.0.0.1
- Quad9 DNS Primer: 9.9.9.9
- Quad9 Secondary DNS: 149.112.112.112
How to Enable DNS over HTTPS (DoH) in Windows 11
Microsoft has introduced a privacy tool called DNS-over-HTTPS in Windows 11 that allows users to perform encrypted DNS lookups to circumvent Internet restrictions and activities.
To enable DNS over HTTPS (DoH) in Windows 11, follow these steps:
- Open Windows 11 “Settings“. You can open it by using the keyboard keys (WIN + I).
- Then select “Network & Internet“. You may have multiple networks you can use, such as WiFi and Ethernet. You can just select the one you are currently using.
- On the right panel, click the “Properties” button.
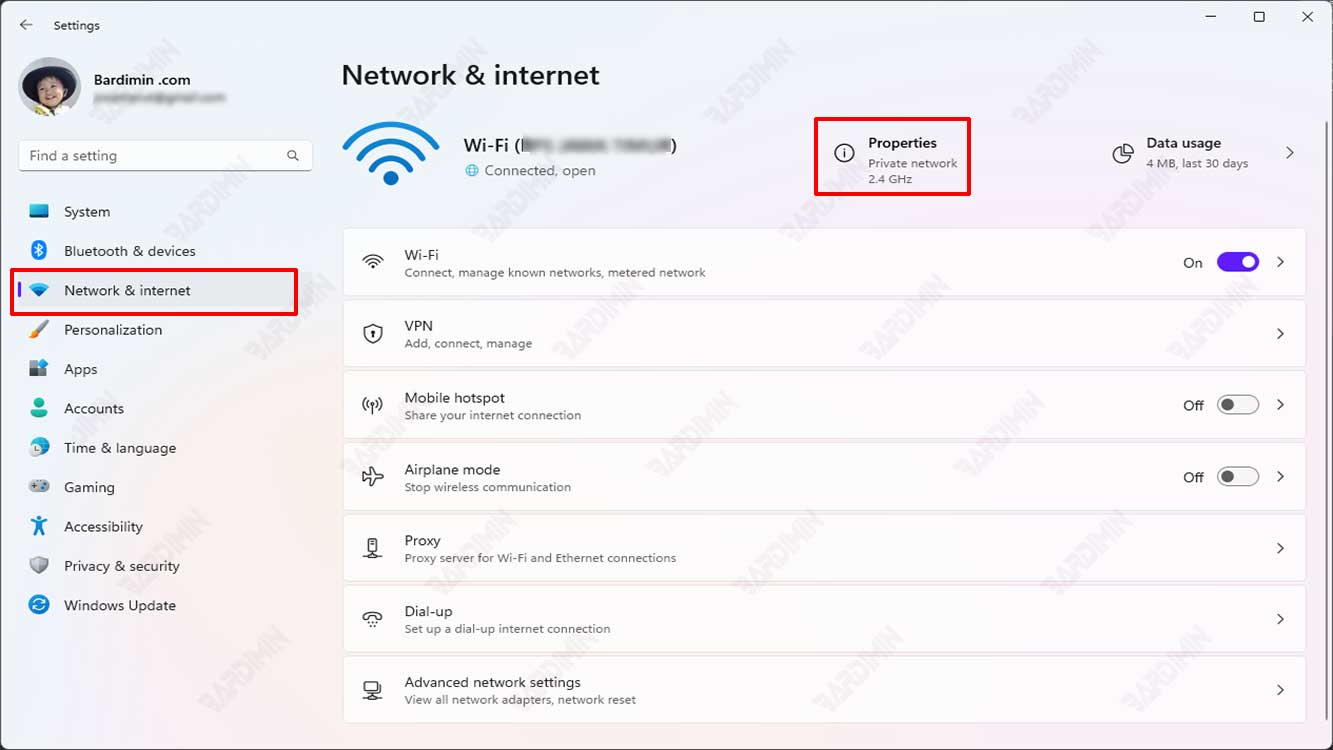
- Then in “DNS server assignment“, click the “Edit” button located next to it.
- In the dialog box that appears, change “Automatic (DHCP)” to “Manual“.
- Then, slide the IPV4 button to the right to enable it.
- Under “Preferred DNS“, enter the IP address of the primary DNS you are using. You can use Google DNS with the IP address: 8.8.8.8
- In “DNS over HTTPS“, select “On (automatic template)“.
- Next, for “Alternate DNS” which is the secondary DNS, fill it in as in “Preferred DNS”. You can use IP: 8.8.4.4 which is Google’s Secondary DNS.
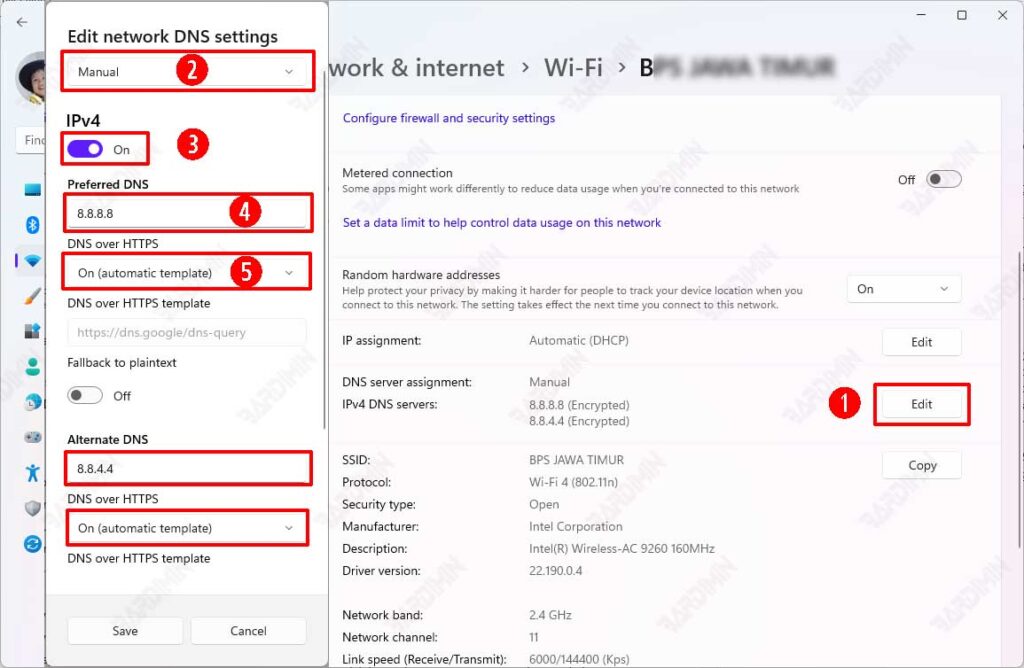
- Click the “Save” button to save the changes.


