Managing PCs using scripts can provide detailed information about various aspects of the system, both local and remote. PowerShell is a very powerful tool for this purpose, and below is a guide on how to use some basic commands to get the necessary system information.
File and Disk Information
To get information about the file and disk structure on your PC, you can use the following command:
Get-Disk and Get-PhysicalDisk:
This command provides a report on the attached disk. The resulting data can be exported to CSV or HTML format using additional commands such as:
| ConvertTo-Html -Title 'Disk Information' | Set-Content E:\DiskReport.htmor
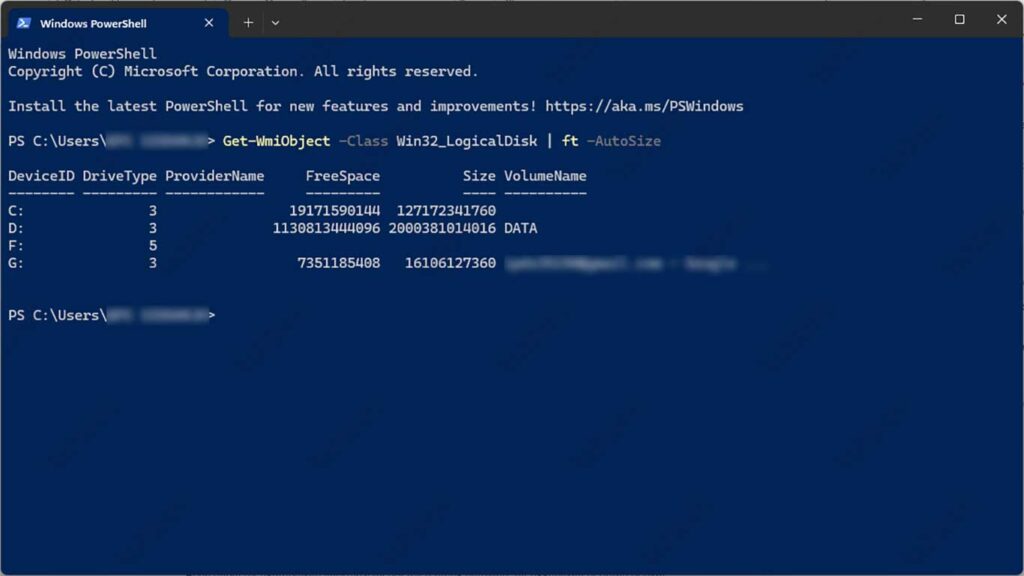
| Export-Csv -NoTypeInformation -Path E:\DiskReport.csvGet-WmiObject -Class Win32_LogicalDisk:
This command displays the partition structure on the local disk. You can also use the additional options of | ft -AutoSize to beautify the data display.
Get-WmiObject -List -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2:
This command lets you see all the resources shared on your PC, including disks, printers, devices, folders, and files.
For more information about file sharing and permissions, you can use the Get-Acl command to see the owner and permissions of a specific folder, for example:
Get-Acl -Path C:\WindowsIf you want to be more detailed, use:
Get-Acl -Path D:\Bardimin\OneDrive\Documents | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Access | Format-Table -AutoSizeHardware and System Information
You can collect detailed information about the hardware using the following commands:
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_BIOS:
Displays information about the UEFI system (BIOS) on the PC. You can also save this information into a CSV file for further analysis.
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_ComputerSystem | Format-List -Property:
This command provides technical information about the PC hardware.
For information about the processor, use:
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_ComputerSystem | Format-List -Property *
Get-CimClass -Namespace Root\CimV2 -ClassName win32*processor*Process and Service Information
To see the apps installed on your PC, use the command:
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_Product | Format-List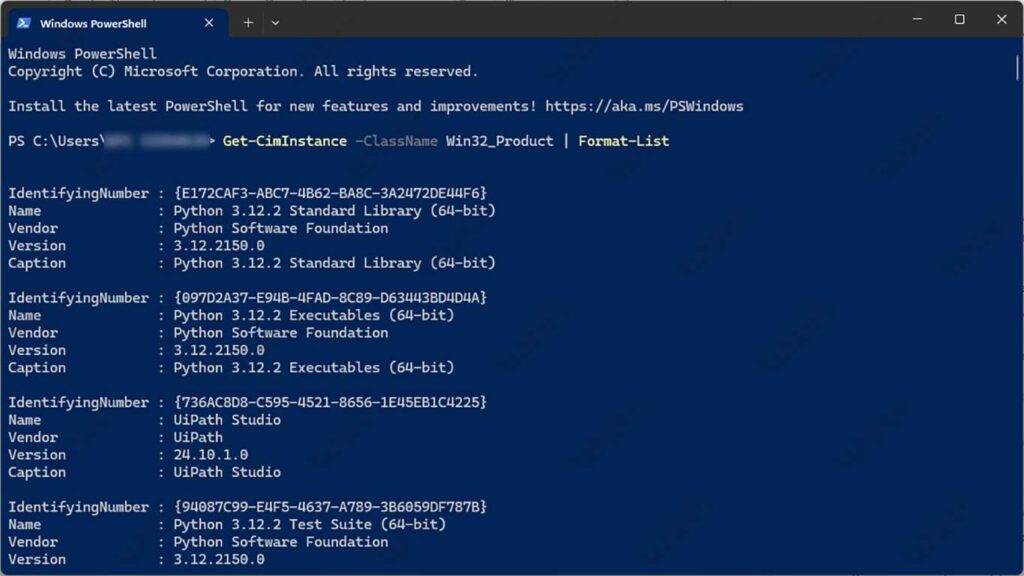
This command is especially useful when diagnosing problems caused by different software versions.
To get information about a process in progress, use:
Get-ProcessAs for the service, the commands used are:
Get-ServiceYou can filter the results by using specific criteria, such as:
- *Get-Service “net”**: Displays services that start with a specific character.
- Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq “Running”}: Displays a list of running services.
By using these commands, you can efficiently and effectively manage and diagnose problems on your Windows system. Be sure to refer to the Microsoft documentation for more information and additional commands that may be needed.
PowerShell also allows you to manage services more effectively. You can stop, start, or disable a specific service using the following commands:
Stopping the Service:
Get-Service -Name “Spooler” | Stop-ServiceGetting Started with the Service:
Get-Service -Name “Spooler” | Start-ServiceDisabling the Service:
Get-Service -Name “Spooler” | Set-Service -StartupType DisabledThese commands are very useful for managing services that may be causing problems with the system. You can also use the Get-Service command with filters to display specific services, for example:
Displaying Running Services:
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq “Running”}Network Information
PowerShell also allows you to collect important network information. Some useful commands include:
Displaying IP Address:
Get-NetIPAddressDisplaying the Routing Table:
Get-NetRouteDisplaying Network Card Information:
Get-NetAdapterDisplaying Firewall Rules:
Get-NetFirewallRuleThese commands help you understand your network configuration and identify potential issues that may exist.
Conclusion
By using PowerShell, you can collect and manage system information in an efficient and structured way. From disk and file information, and hardware details, to service and network management, PowerShell provides powerful tools for system administrators.
With a good understanding of these commands, you can proactively troubleshoot issues and ensure the system is running properly. For further exploration, you can refer to Microsoft’s official documentation which provides in-depth information about each command that has been discussed.


