This article discusses practical techniques for generating large amounts of random test data in a MySQL database. You will learn how to create stored functions and procedures to automatically populate tables with thousands of rows of data. This method is very useful for performance testing, load simulation, and application development that requires realistic datasets.
Database application development requires testing that closely resembles real conditions. A MySQL random data script is an efficient solution for creating large-scale test data. This simulation helps developers measure application performance across various scenarios. You can test from ideal conditions to high loads.
This technique uses stored procedures and custom MySQL functions. This approach provides high flexibility in determining the quantity and format of data. Additionally, the data population process becomes faster and more consistent. Manual methods are no longer needed to create large amounts of test data.
Steps to Create a Table for Random Data
Before creating the script, first prepare the database table. Create a table with a structure that suits your testing needs. The following example shows a simple table with three columns.
CREATE TABLE `random_data` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
`column01` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
`column02` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;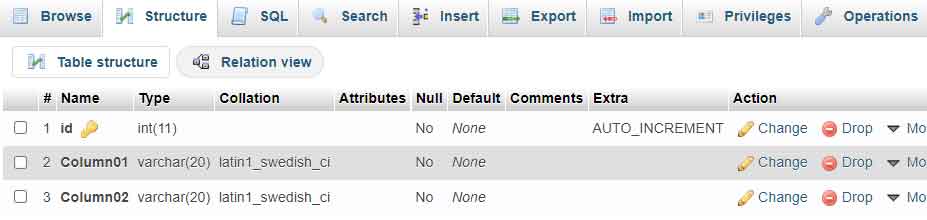
Ensure you have selected the correct database before running the above command. The id column is set as a primary key with auto increment. This way, each row of data will have a unique identifier automatically.
Creating a Random String Generation Function
The first step is to create a function that generates random strings. This function will be called repeatedly by the main procedure. Here is the implementation of the random_string function you can use.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION `random_string`(length INT)
RETURNS VARCHAR(255) DETERMINISTIC
BEGIN
DECLARE chars VARCHAR(62) DEFAULT 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789';
DECLARE result VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
WHILE i < length DO
SET result = CONCAT(result, SUBSTRING(chars, FLOOR(1 + RAND() * 62), 1));
SET i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
RETURN result;
END$$
DELIMITER ;This function will generate a random string consisting of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numbers. The length parameter determines the desired string length. You can adjust the character set according to specific needs.
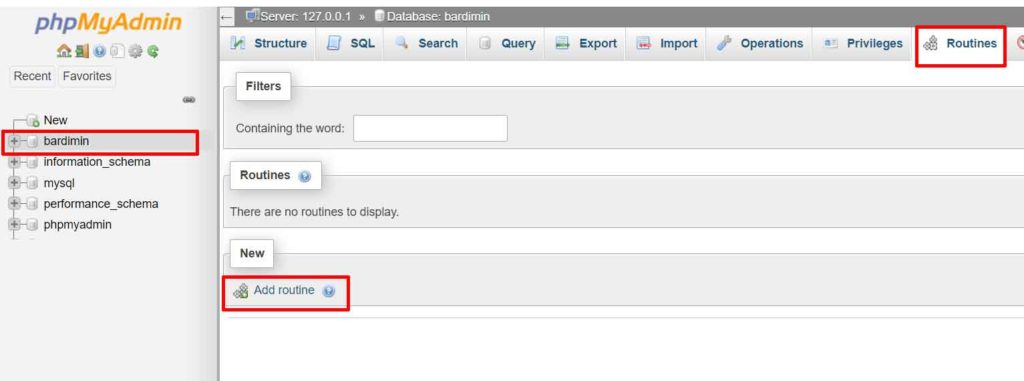
Implementation via phpMyAdmin
- Access phpMyAdmin and select your target database.
- Open the “Routines” tab at the top of the interface.
- Click the “Add routine” button to create a new function.
- Select the “FUNCTION” type and enter the code above.
- Save the function with the name
random_string.
Creating a Procedure for Bulk Data Insertion
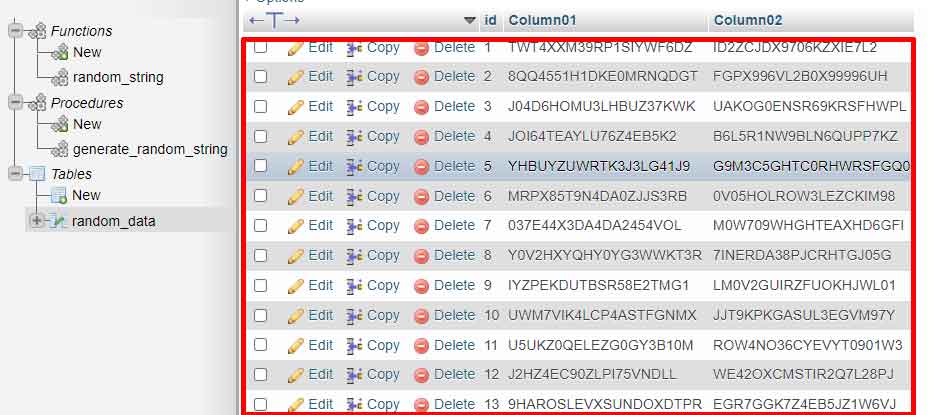
Once the function is available, create a stored procedure that performs bulk data insertion. This procedure uses loops to add rows repeatedly. You can adjust the number of iterations according to your needs.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `generate_random_data`(IN row_count INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
WHILE i < row_count DO
INSERT INTO random_data (column01, column02)
VALUES (random_string(20), random_string(20));
SET i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
END$$
DELIMITER ;The above procedure accepts a row_count parameter to determine the number of data rows. Thus, you can generate data in flexible quantities, from hundreds to millions of rows. This procedure calls the random_string function for each column that requires random data.
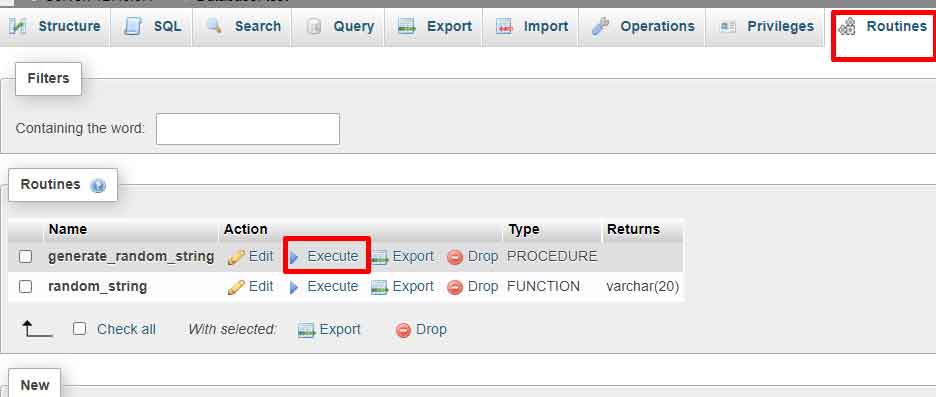
Executing the Stored Procedure
- In phpMyAdmin, open the “Routines” tab again.
- Select the
generate_random_dataprocedure from the list. - Click the “Execute” button next to the procedure name.
- Enter the desired number of rows when prompted for the parameter.
- Click the “Go” button to run the procedure.
Optimization and Technical Considerations
For inserting very large amounts of data, consider the following optimizations:
- Temporarily disable indexes: Turn off table indexes before insertion, then re-enable them after completion. This speeds up the bulk insert process.
- Use a single transaction: Start with
START TRANSACTIONand end withCOMMIT. This technique reduces transaction log overhead. - Batch processing: Divide the insert into several batches to avoid timeouts and monitor progress.
- Monitor resources: Monitor CPU and memory usage during the process. Adjust batch size based on server capacity.
For example, to insert 1 million rows of data, you can divide it into 10 batches of 100,000 rows each. This way, you can monitor progress and avoid failures due to timeouts.
By following this guide, you can create an effective MySQL random data script for testing needs. This technique not only saves time but also provides more realistic test data. For more information on stored procedures, visit the official MySQL documentation. Always conduct testing in a development environment before applying in production.


