Duplicate data can compromise database integrity and performance. This article explores an effective method to delete duplicate rows in MySQL using the DELETE JOIN technique. This step-by-step guide is designed for technicians, developers, and IT professionals who prioritize data cleanliness.
Encountering duplicate rows in MySQL tables is a common challenge many face. This condition can lead to inaccurate query results and increased system load. Therefore, the ability to delete duplicate rows in MySQL is an essential skill. This tutorial will guide you through resolving this issue with an efficient and proven method.
Preparing a Sample Data Table
Before practicing the deletion method, you need to set up a test environment. Create a table named duplicate_row with the following structure and initial data in your database.
CREATE TABLE `duplicate_row` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`refID` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`data` varchar(7) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;Next, insert sample data containing duplicate values in the refID column.
INSERT INTO `duplicate_row` (`id`, `refID`, `data`) VALUES
(1, 3526, 'aaaaaaa'),
(2, 3527, 'bbbbbbb'),
(3, 3528, 'ccccccc'),
(4, 3529, 'ddddddd'),
(5, 3527, 'eeeeeee'),
(6, 3528, 'fffffff'),
(7, 3527, 'ggggggg');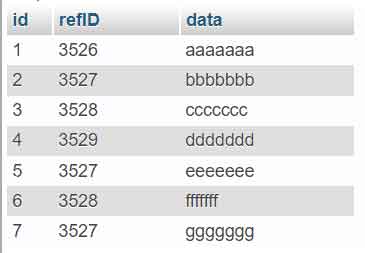
Tutorial: Delete Duplicate Rows in MySQL with DELETE JOIN
The DELETE JOIN method is one of the most efficient ways to handle duplicates. This technique works by joining the table to itself. This allows you to identify and remove redundant rows based on specific criteria.
- Open your phpMyAdmin application and select the database containing the
duplicate_rowtable. - Navigate to the SQL tab to run commands directly.
- Copy and paste the following SQL query into the available text field.
DELETE t1 FROM duplicate_row t1
INNER JOIN duplicate_row t2
WHERE
t1.refID = t2.refID AND
t1.id > t2.id;Important: The query above will retain the row with the smallest
idvalue for each duplicate group inrefID. Rows with a largeridwill be deleted.
- Click the Go button to execute the command.

Once the query runs successfully, only one row for each unique refID value will remain. For example, for refID 3527, only the row with id=2 is kept. This process is effective for deleting duplicate rows in MySQL on a reasonably large scale.
Important Tips and Considerations
Before running any deletion command, always create a backup of your table or database first. This is a standard safety precaution. Additionally, ensure you have identified the correct column(s) as the reference for duplication.
For more complex scenarios, such as duplication based on multiple columns, you can add conditions to the WHERE clause. Always test the query with a SELECT statement first to ensure the results match your expectations. You can also refer to the official MySQL documentation for more advanced techniques.
Conclusion
Maintaining clean data free from duplication is a crucial part of database administration. The DELETE JOIN method described provides a direct and powerful solution. By following the practical steps above, you can promptly address duplicate issues and ensure your database’s quality and performance remain optimal.


