In networking, the right choice of switches is essential to ensure optimal performance and security. The two types of switches that are often compared are Layer 2 and Layer 3. Let’s explore the differences and how they affect the user experience.
Layer 2 Switches and Layer 3 Switches are network devices used to manage data traffic within computer networks. Although both have the same basic function when it comes to facilitating communication between devices, they operate on different layers in the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which affects how they work and function.
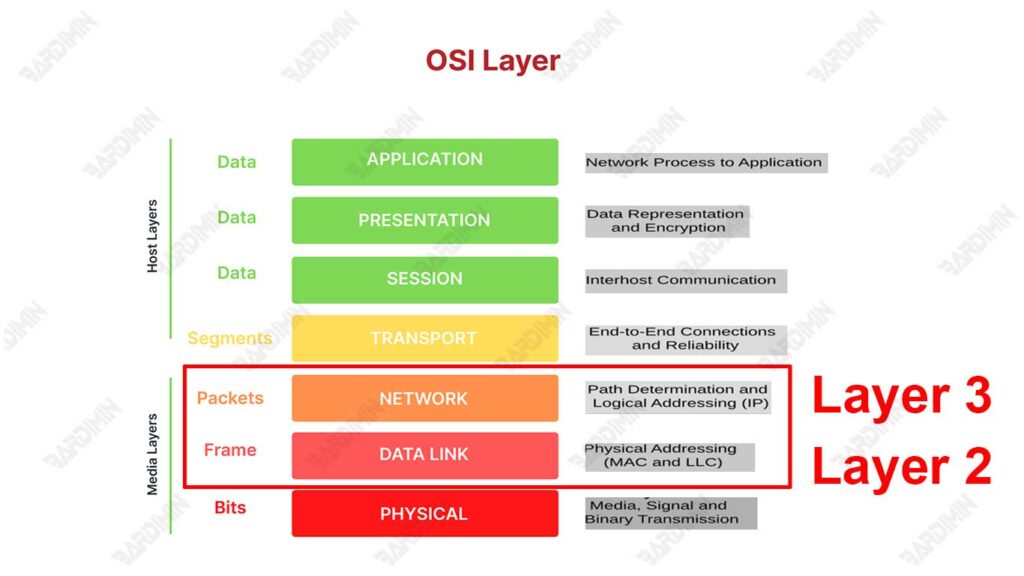
What are Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches?
The main difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches lies in the level of the OSI model in which they operate. The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a standard framework that divides the network communication process into seven layers.
Layer 2 switches operate on Layer 2 (Data Link Layer). At this layer, the switch uses the MAC (Media Access Control) address to identify the device and pass data between devices within the same network segment. Have the ability to create and manage VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) for network segmentation.
Layer 3 switches operate on Layer 3 (Network Layer). At this layer, the switch uses IP (Internet Protocol) addresses to identify devices and pass data between different network segments, even between different networks (for example, between different VLANs or subnets). It can run routing protocols such as OSPF, EIGRP, and BGP, allowing for more complex data route management.
Layer 2 Switch Basics
Layer 2 Switches are network devices that operate on the Data Link Layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model. Its function is to pass data in frame form based on the MAC (Media Access Control) address of the source and destination of that frame.
Layer 2 Switches are often used in local area networks (LANs) to connect devices within a single network segment, allowing for fast and efficient communication between devices.
How Layer 2 Switches Work
Layer 2 Switches work by using MAC addressing tables to determine where data frames should be forwarded. Here’s how a Layer 2 Switch works:
MAC Switching and Addressing
Switching:
- When a data frame enters one of the switch ports, the switch reads the destination MAC address of the frame.
- The switch checks the MAC addressing table it has in it to find the port that matches the destination MAC address.
- If the destination MAC address is found in the table, the frame is forwarded to the appropriate port.
- If the destination MAC address is not found, the switch will broadcast the frame to all ports except the origin port.
MAC Addressing:
- Each device in the network has a unique MAC address.
- The switch uses this MAC address to identify the device and make switching decisions.
Bridging
Layer 2 Switches also function as bridges, which means they can connect two or more network segments and make them work as one logical network. Bridging allows different segments to communicate with each other as if they were in the same network.
Advantages of Using Layer 2 Switches
Simple and Efficient
Layer 2 Switches are relatively easy to implement and manage. MAC address-based switching operations are simple and fast, making Layer 2 Switches an efficient solution for local networks.
Low latency
Since it only operates on the Data Link Layer, the latency generated by Layer 2 Switches is very low. This low latency is important for applications that require fast responses, such as VoIP (Voice over IP) and video streaming.
Disadvantages of Layer 2 Switches
Limited to MAC Addressing
Layer 2 Switches can only use MAC addresses to make switching decisions. Unable to understand or process information at higher layers such as IP addresses.
Does not support routing
Layer 2 Switches cannot route between different networks or subnets. For routing, another device such as a Layer 3 Switch or router is required, which can forward packets based on IP addresses.
Layer 3 Switch Basics
A Layer 3 Switch is a networking device that combines the switching functionality of Layer 2 with the routing capabilities of Layer 3 in the OSI model. This means that Layer 3 Switches can forward data packets based on IP addresses and supports routing between networks.
In other words, Layer 3 Switches are capable of managing traffic not only within a single local area network (LAN) but also between different subnets or VLANs.
How Layer 3 Switches Work
Layer 3 Switches work by combining switching and routing capabilities to manage data traffic. Here’s how the basic Layer 3 Switch works:
IP Routing and Addressing
Layer 3 Switches use routing tables to make routing decisions based on the IP addresses of data packets. When a data packet enters the switch, it checks the destination IP address and determines the best route to forward the packet.
Each device in the network has a unique IP address. Layer 3 Switches use these IP addresses to identify devices and make routing decisions.
Use of Routing Protocols such as OSPF, BGP
Layer 3 Switches can run various routing protocols such as OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol). OSPF is used to find the best route in a large network by calculating the shortest path to the destination. BGP is used for routing between different networks, such as between two internet service providers (ISPs).
Advantages of Using Layer 3 Switch
Supports Routing Between Networks
Layer 3 Switches are capable of routing between different networks or subnets, allowing for more efficient and structured communication. This is particularly useful in large networks where segmentation and management of traffic between subnets or VLANs is required.
More Flexible and Scalable
Layer 3 Switches offer greater flexibility in managing and regulating network traffic. Enable the growth of larger and more complex networks with support for dynamic routing and advanced routing protocols.
Disadvantages of Layer 3 Switches
More Complex and Expensive
Layer 3 Switches are generally more expensive than Layer 2 Switches due to their more advanced capabilities and more powerful hardware. Requires greater investment in terms of purchase and maintenance costs.
Requires More Complicated Configuration
Layer 3 Switches require more complex configurations and specialized expertise for management and maintenance. The use of routing protocols and routing table settings requires an in-depth understanding of networking and routing.
Detailed Comparison between Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
Main Differences in Architecture
Switching vs. Routing
Layer 2 Switch:
- Switching: Operates on the Data Link Layer by using MAC addresses to forward data frames within the local network (LAN).
- MAC Addressing: Uses the MAC address to determine the path of the data frame to the exact destination.
Layer 3 Switch:
- Routing: Operates at the Network Layer by using IP addresses to forward data packets and route between networks.
- IP Addressing: Uses IP addresses to manage the routing of data packets, allowing communication between different subnets or VLANs.
Performance and Scalability
Latency and Throughput
Layer 2 Switch:
- Latency: Offers low latency due to fast and simple switching operations.
- Throughput: It generally has high throughput in a LAN environment due to the lack of routing overhead.
Layer 3 Switch:
- Latency: It may have slightly higher latency due to the addition of the routing process, although it is still fast and efficient.
- Throughput: It can handle high throughput while supporting routing between networks, ideal for large and complex networks.
Traffic Handling Capacity
- Layer 2 Switch:
- Ideal for high-traffic networks within a single network segment.
- Limited to handling traffic within a single VLAN or subnet.
- Layer 3 Switch:
- Able to handle larger and more complex traffic by routing between subnets or VLANs.
- Supports efficient traffic distribution within large networks.
Capabilities and Functions
VLAN
- Layer 2 Switch:
- Supports VLANs for network segmentation and traffic isolation.
- Layer 3 Switch:
- Supports VLANs and can route between VLANs, improving flexibility and traffic management.
QoS (Quality of Service)
- Layer 2 Switch:
- Supports basic QoS for traffic prioritization in the local network.
- Layer 3 Switch:
- Supports more advanced QoS, allowing for traffic prioritization based on application, user, or data type to ensure optimal performance.
Multicast
- Layer 2 Switch:
- Supports multicast with protocols such as IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) to manage multicast groups.
- Layer 3 Switch:
- Supports multicast routing with protocols such as PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast), allowing for efficient distribution of multicast traffic across the network.
Cost and Complexity
Hardware Pricing and Operating Costs
- Layer 2 Switch:
- They are generally cheaper in terms of hardware and operational costs due to their simpler functionality.
- Layer 3 Switch:
- More expensive due to additional routing capabilities and more advanced hardware, requiring greater investment.
Human Resource Needs and Expertise
- Layer 2 Switch:
- Requires basic expertise in network configuration and management, easier to manage.
- Layer 3 Switch:
- Requires specialized expertise in routing and managing more complex networks.
- Requires a deep understanding of routing protocols and more complex configurations.
When to Use Layer 2 Switches
Small and Medium Networks
Layer 2 Switches are ideal for use in small to medium-sized networks where routing between subnets or VLANs is not required. Some examples of scenarios include:
- Small Office Home Office (SOHO):
- Connecting devices such as computers, printers, and servers in a single network segment.
- Enables fast and efficient communication between devices without the need for complex routing.
- Local Network of Small Schools or Campuses:
- Connecting computers, storage devices, and internet access in a single network segment.
- Provide reliable and easy-to-manage connectivity for the educational environment.
- Small Factory or Industry Network:
- Connecting machines, sensors, and control systems in a single network.
- Ensuring real-time communication that is critical to industrial operations.
Low Latency Requirements
Layer 2 Switches are also very useful in scenarios where low latency is a top priority. Some examples include:
- VoIP (Voice over IP) applications:
- Provides a low-latency connection for clear, delay-free voice communication.
- Video and Multimedia Streaming:
- Connect streaming devices with minimal latency for a smooth, buffer-free viewing experience.
- Online or E-sports Games:
- Connect a low-latency gaming console or computer to ensure fast response and competitive gaming.
Layer 2 Switch Implementation Example
Small Offices with Basic Connection Needs
In a small office with fewer than 50 devices, Layer 2 Switches can be used to connect all of those devices in a single network. Here is an example of implementation:
- Connected Devices: Computers, printers, file servers, and Wi-Fi access points.
- Configuration:
- All devices are connected to a Layer 2 Switch.
- VLANs can be used for segmentation, for example separating employee and guest networks.
- Basic QoS can be implemented for the prioritization of VoIP and video traffic.
High School with Local Network
In a high school, Layer 2 Switches can be used to connect laboratory computers, storage devices, and school management systems in a single local network. Here is an example of implementation:
- Connected Devices: Laboratory computers, school servers, storage devices, network printers.
- Configuration:
- Layer 2 Switches are housed in the server room and connect to all devices via Ethernet cables.
- VLANs can be used to separate administrative networks and student networks.
- IGMP is used to support multicast in online classes or educational video streaming.
Small Industries with Real-Time Needs
In a small factory, Layer 2 Switches can be used to connect machines, sensors, and control systems. Here is an example of implementation:
- Connected Devices: Production machines, sensors, control systems, operator computers.
- Configuration:
- Layer 2 Switches are housed in the control room and connected to all devices via industrial Ethernet cables.
- VLANs are used to separate the control network and the administration network.
- QoS is implemented for prioritizing industrial control traffic that requires very low latency.
When to Use Layer 3 Switches
Large and Complex Networks
Layer 3 Switches are ideal for use in large and complex networks where routing needs between subnets or VLANs are required. Some examples of scenarios include:
- Large Corporations:
- Connect different departments that may be spread across multiple locations or floors.
- Ensures efficient communication between different subnets or VLANs.
- University Campus:
- Connecting various faculties, laboratories, and dormitories.
- Allows routing of traffic between subnets to support academic and administrative needs.
- Data Center:
- Manage traffic between servers, storage, and external networks.
- Provides fast and reliable routing to support business-critical applications.
Inter-Network Routing Needs
Layer 3 Switches are also very useful in scenarios where routing needs between networks or subnets are critical. Some examples include:
- Networks That Require Isolation and Segmentation:
- Isolate traffic between employee networks, guests, and IoT devices for security and management reasons.
- Use VLANs and route between VLANs to optimize network performance.
- Networks That Require High Redundancy and Reliability:
- Implement routing protocols such as OSPF and BGP to ensure the best routing and provide redundancy.
- Supports automatic failover in case of network failure.
Layer 3 Switch Implementation Example
Large Companies with Separate Departments
In a large company with multiple departments spread across various floors or buildings, Layer 3 Switches can be used to manage routing between subnets and VLANs. Here is an example of implementation:
- Connected Devices: Computers, printers, servers, Wi-Fi access points in various departments.
- Configuration:
- Each department has its VLAN for traffic isolation.
- Layer 3 Switches route between VLANs to enable communication between departments.
- QoS is implemented for prioritizing critical traffic such as VoIP and business applications.
University Campus with Many Faculties
On a university campus, Layer 3 Switches can be used to connect various faculties, laboratories, and dormitories, ensuring efficient communication between subnets. Here is an example of implementation:
- Connected Devices: Laboratory computers, faculty servers, storage devices, network printers.
- Configuration:
- Each faculty has its subnet or VLAN.
- Layer 3 Switches route between subnets to support academic and administrative needs.
- Multicast routing is used to support online lectures and streaming educational videos.
Data Centers with High Redundancy Needs
In a data center, Layer 3 Switches can be used to manage traffic between servers, storage, and external networks, ensuring high performance and redundancy. Here is an example of implementation:
- Connected Devices: Servers, storage devices, firewalls, routers.
- Configuration:
- Layer 3 Switches are used for routing between subnets that connect various security zones within a data center.
- Routing protocols such as OSPF and BGP are used to ensure the best routing and provide redundancy.
- QoS is implemented for traffic prioritization of critical business applications and cloud services.
Conclusion
In choosing between Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switch, we need to understand the differences and needs of the network we want to build. Here is a summary and suggestions regarding the use of both:
Layer 2 Switch:
- Works on the data link layer (OSI model).
- It uses a MAC (Media Access Control) address to direct the data flow.
- Suitable for less complex local area networks (LANs).
- It does not have routing capabilities.
- Efficient and cheaper.
- Quick to configure.
- Used to connect multiple devices in the office or home.
Layer 3 Switch:
- Works on the network layer (OSI model).
- It uses the IP (Internet Protocol) protocol to direct data streams based on IP addresses.
- Able to perform routing functions, connecting between subnets or inter-VLANs in more complex networks.
- A combination between a layer 2 switch and a router.
- Suitable for wide networks with multiple subnets or VLANs.
- Handle multiple data streams efficiently and at high speed.
If you have a small local area network without complex routing needs, Layer 2 Switches will suffice.
If you have a wide network with multiple subnets or VLANs and need routing capabilities, then Layer 3 Switches are a better choice.


