NAT (Network Address Translation) is a mechanism that allows devices with private IP addresses to connect to public networks, such as the Internet. The existence of NAT is crucial in contemporary networks given the limited number of public IP addresses, while the demand for internet-connected devices is constantly increasing.
NAT works by translating private IP addresses into public IP addresses so that devices in a private network can access the Internet without needing their respective public IP addresses. Thus, NAT becomes an efficient solution for using IP addresses and protects private networks from direct access by outsiders.
Main Purpose of NAT
NAT hides a device’s private IP address from external networks, thus increasing protection against potential threats.
By hiding the network’s internal structure, NAT helps reduce the likelihood of direct attacks on devices.
2. Efficiency in the Use of IP Addresses
NAT allows multiple devices to share one or more public IP addresses, thus reducing the need for limited public IP addresses. This is very useful in dealing with the limitations of IPv4 addresses.
3. Ease in Network Administration
NAT provides flexibility in network management as it does not rely entirely on ISPs for IP allocation.
Administrators can easily manage private networks without publishing each device to the internet.
Types of NAT
1. Static NAT
Static NAT is a network address translation method where one private IP address is always translated into one specific public IP address. In Static NAT, the relationship between a private IP address and a public IP address is permanent, which means it does not change over time.
Static NAT is commonly used on devices that require direct access from a public network, such as web servers, email servers, or other devices that require an IP address that can be accessed from the outside.
Examples of Use on Internal Servers
For example, a company has an internal server with a private IP address 192.168.11.10. These servers need to be accessed by users from the internet. Using Static NAT, network administrators can configure the public IP address 203.0.113.10 to always be connected to the private IP address 192.168.11.10.
This allows the server to remain accessible from the internet using a public IP address without having to disclose its private IP address.
Advantages of Static NAT
Static NAT provides a consistent public IP address to devices on a private network, making it easy to manage network access.
Since public IP addresses are fixed, Static NAT simplifies the registration process in DNS. For example, the www.contohperusahaan.com domain name can be associated with a server’s public IP address via DNS.
With permanent linkage, devices such as servers can be accessed at any time without the need to change the IP address configuration.
Static NAT is an ideal solution for network devices that require direct connectivity to the internet while maintaining the security of the internal network structure.
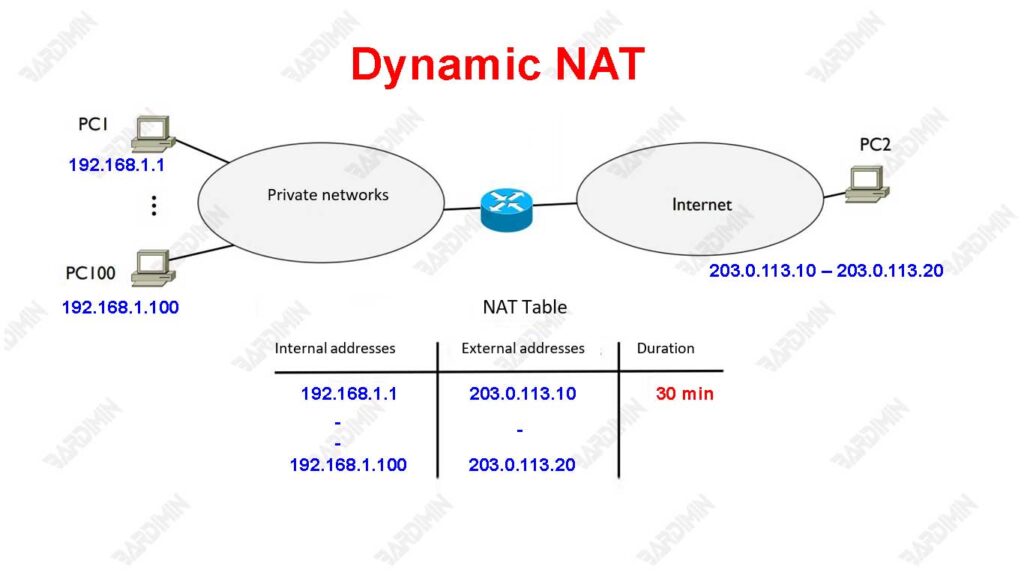
2. Dynamic NAT
Dynamic NAT is a method of network address translation in which a private IP address is dynamically translated into one of the available public IP addresses from a predefined range. Unlike Static NAT, Dynamic NAT does not permanently associate between private and public IP addresses. In contrast, devices in a private network will temporarily obtain a public IP address only when needed, such as when the device is attempting to access the internet.
Example Scenario: Client Connection with a Private Address to the Internet
Suppose a small office has a network with multiple devices that each have a private IP address, such as 192.168.11.2, 192.168.11.3, and so on. The routers on that network have been configured with Dynamic NAT and have a range of available public IP addresses, for example, 203.0..113.10 – 203.0.113.20.
When one of the devices, e.g. 192.168.11.2, attempts to access the internet, the router will dynamically assign one of the public IP addresses of the available range, e.g. 203.0.1113.10, to be used during the connection session. The address will be released once the connection is complete so that it can be used by other devices.

Advantages of Dynamic NAT
Dynamic NAT allows multiple devices on a private network to share a small range of public IP addresses. This is very efficient, especially if only a small number of devices require internet access at the same time.
By provisioning public IP addresses temporarily, Dynamic NAT helps overcome the limitations of IPv4 addresses by utilizing public addresses interchangeably.
Dynamic NAT is ideal for networks with many client devices that rarely access the internet at the same time, such as in a small office or home network.

