The size of MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is a crucial aspect of network settings that is often overlooked. MTU determines the maximum size of a data packet that can be transmitted over the network without needing to be broken down into smaller fragments.
Think of the MTU as a container truck. The larger the container, the more goods can be transported in one trip. Likewise, with MTU, the larger the size, the more data can be transmitted in one package.
Proper MTU settings are crucial because they affect the efficiency and speed of data transmission.
The optimal MTU size can:
- Improves Network Performance: With the appropriate MTU size, data can be delivered in large packets that reduce overhead and speed up transmission.
- Minimizes Fragmentation: Optimal MTU settings prevent packet fragmentation which can slow down data transfer speeds and reduce network efficiency.

How MTU Works
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the maximum size of a data packet that can be transmitted over a network without being broken down into smaller fragments. MTU is determined by a network device, such as a router or switch, and is measured in bytes. For example, the standard MTU size for Ethernet is 1500 bytes.
How does MTU work in networking?
- Data Packet Delivery: When data is sent over a network, it is broken down into smaller packets. The MTU specifies the maximum size limit for these packages.
- Fragmentation: If the size of a data packet exceeds the MTU, it will be broken down into smaller fragments. This process is known as fragmentation.
- Reassembly: On the receiver side, these fragments are put back together into a whole data packet before being passed on to the application that needs it.
When a device (such as a computer, router, or switch) wants to transmit data over a network, it is wrapped in data packets. Each packet has a header that contains information such as destination address, source address, and data type. The maximum size of the data portion in this packet is called MTU.
If the size of the data you want to send is greater than the MTU, the data will be broken down into smaller packets, each with a size that does not exceed the MTU. This process of breaking the package is called fragmentation. On the receiving side, the fragmented packets will be rearranged into a whole piece of data.
The Role of MTU in the Network
The size of the MTU has a significant influence on network performance and data transmission efficiency. Some of the important roles of MTUs in networks are as follows:
- Reduced Overhead: Larger data packets can reduce the number of packets that need to be sent, thereby reducing the overhead associated with sending small packets. This can improve the efficiency of the network.
- Prevents Excessive Fragmentation: By setting the MTU accordingly, packet fragmentation can be minimized. Excessive fragmentation can slow down data transmission and increase the likelihood of errors.
- Speeds Up Data Transmission: An optimal MTU allows data to be sent in large packet sizes, speeding up the transmission process. This is important for applications that require fast data transfer, such as video streaming or online gaming.
- Reduced Latency: The right MTU size can reduce the time it takes to send and receive data packets, thereby reducing latency or time lag in network communication.
- Improves Security: The right MTU size can help prevent attacks on the network, such as fragmentation attacks that attackers can leverage to send malicious data packets.
Simple Example:
Imagine you want to send a large video file over the internet. If your network’s MTU is small, the video file will be broken down into many small pieces. Each piece has to pass through the router and switch separately, which can cause the video to become stuttering or even not play smoothly.
Why Is Determining the Optimal MTU Size Important?
Determining the optimal MTU size is an important step in optimizing your network’s performance. The right MTU can provide several significant benefits, including:
Increase Internet Speed
An MTU that is too small will cause the data packet to be fragmented frequently. The process of fragmenting and reassembling packages takes additional time, which can slow down data transfer. With an optimal MTU, fragmentation can be minimized, so data can be transmitted faster.
Larger data packets (with higher MTUs) contain less overhead (additional information in the packet header). This means more data can be delivered in a single packet, making bandwidth usage more efficient.
Reduce Latency and Lost Packets
As mentioned earlier, fragmentation can increase latency. With an optimal MTU, latency can be suppressed, resulting in better network responsiveness. This is especially important for latency-sensitive applications, such as online gaming, video calls, and streaming.
Fragmentation can increase the risk of packets being lost in transit. Lost packages must be resented, which can cause delays and decreased performance. The right MTU can reduce the risk of packet loss.
Network Security
Some types of network attacks take advantage of fragmentation to hide malicious traffic. By setting the MTU correctly, you can prevent this kind of attack.
A stable network is a secure network. Optimal MTU can improve network stability, thereby reducing the risk of interference that attackers can take advantage of.
Other Factors to Consider
- Connection Type: The type of internet connection you use (DSL, cable, fiber optic) can affect the optimal MTU that can be used.
- Network Devices: Routers, switches, and other network devices have a maximum MTU supported. The MTU you set must not exceed the maximum value supported by the device.
- Network Protocols: Some network protocols have specific MTU requirements.
How to Determine the Optimal MTU:
- Ping with Don’t Fragment Options: You can use the ping command with the “-f” (don’t fragment) to find out the maximum MTU supported by your network path.
- Use Specialized Tools: Several specialized tools can be used to measure MTU, such as PathPing on Windows or traceroute on Linux.
- Consult your ISP: You can also consult your internet service provider for recommendations regarding the optimal MTU.
Steps to Determine the Optimal MTU Size
Preparation
Before conducting the MTU test, several equipment and preparations need to be done:
- Stable Internet Connection: Make sure your internet connection is stable and there are no interruptions.
- Computer Device: Prepare the computer or laptop that will be used to perform the MTU test.
- Access to the Router: Make sure you have access to the router’s settings, either through the web interface or the router manager app.
- Network Test Tool: You will need a network tool or utility, such as Command Prompt on Windows, Terminal on macOS, or Terminal on Linux.
Method Ping Test
The steps to perform the Ping Test to determine the optimal MTU size are as follows:
- Open Command Prompt or Terminal:
- Windows: Press Win + R, type cmd, and then press Enter.
- macOS and Linux: Open Terminal from the app or use the shortcut Ctrl+Alt+T (Linux).
- Type Command Ping: Use the ping command with the options -f (set the Don’t Fragment bit) and -l (specify the packet size) to send a data packet of a specific size without fragmentation. Start with a packet size of 1472 bytes (since the MTU size of 1500 bytes includes a 28-byte IP header).
ping [ip_address] -f -l 1472
- Reduce Package Size: If you receive the message “Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set”, reduce the package size by 10 bytes and repeat the command.
ping [ip_address] -f -l 1462
- Find Maximum Size Not Fragmented: Repeat step 3 until you find the maximum size that does not generate an error message. Add 28 bytes to determine the optimal MTU size.
ping [ip_address] -f -l [largest_size]
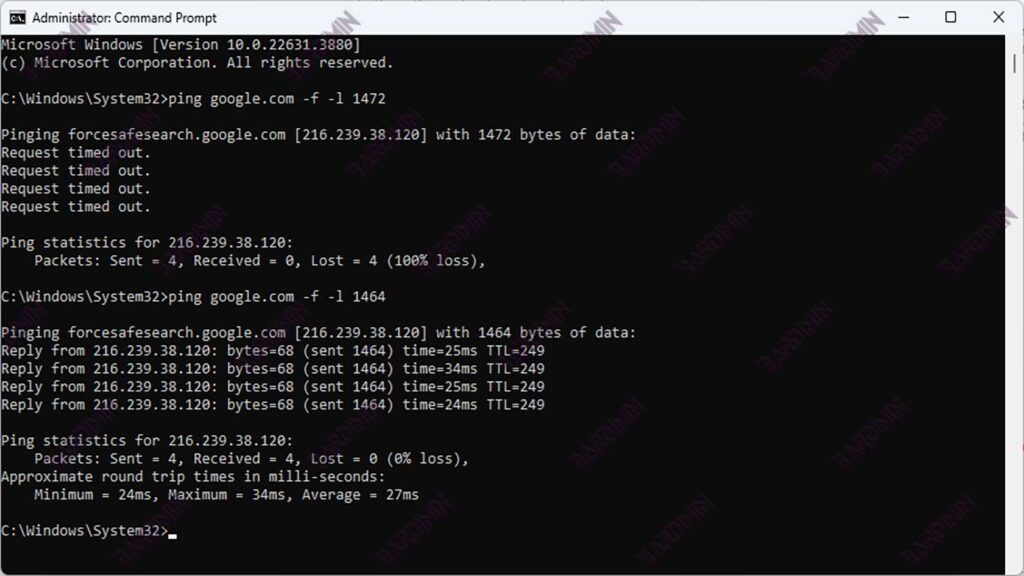
Practical Examples
- Windows:
ping google.com -f -l 1472
- macOS:
ping -D -s 1472 google.com
- Linux:
ping -M do -s 1472 google.com
Addressing Error Messages
If you receive an error message like “Request timed out” or “Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set”:
- Reduce Package Size: Reduce the size of the package being tested until the error message disappears.
- Check Connection: Make sure there is no disruption to your internet connection.
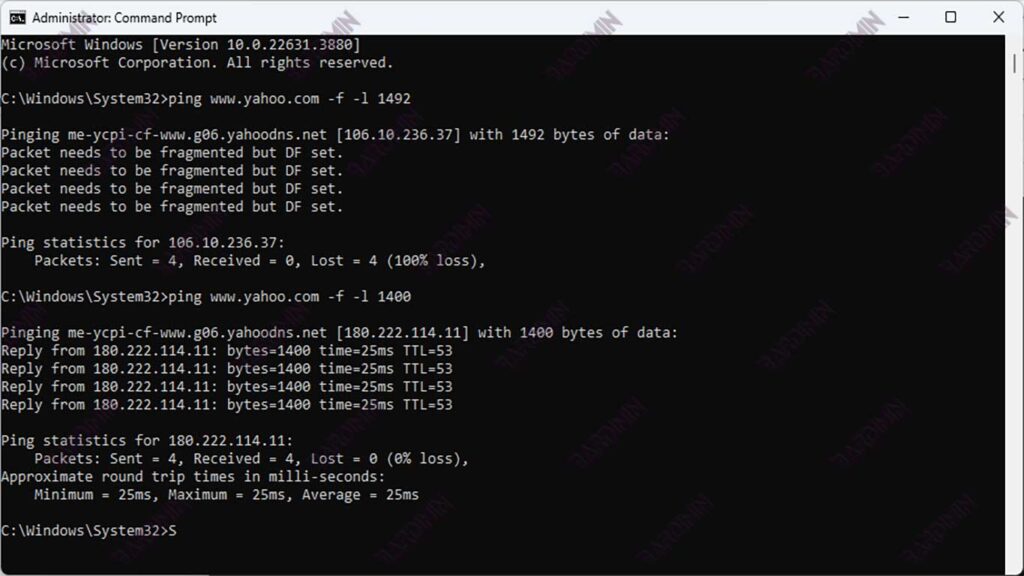
Destination host unreachable: This means that the package cannot reach its destination. There may be a problem with the connection or the IP address you are using.
Packet too big: This means that the package size exceeds the MTU. Make a note of the size of the last successful packet before this message appears.
Fragmentation needed and DF set: This means that the package must be broken into fragments, but the don’t fragment (DF) option is enabled.
Testing and Setting MTU on the Router
After determining the optimal MTU size, the next step is to set up the MTU on your router. Here’s a general guide to some types of routers:
- Access Router Settings:
- Open a web browser and enter the IP address of the router (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Enter your username and password to access the settings interface.
- Navigate to MTU Settings:
- Look for the Network Settings, WAN Settings, or Advanced Settings options.
- Find the section to set up MTU.
- Set MTU Size:
- Enter the optimal MTU size that you have determined.
- Save the changes and reboot the router if needed.
Example Setup
- Netgear:
- Log in to the router’s web interface.
- Navigate to Advanced > Setup > WAN Setup.
- Set MTU Size and save the changes.
- TP-Link:
- Log in to the router’s web interface.
- Navigate to Network > WAN.
- Set MTU Size and save the changes.
By following the steps above, you can determine and set the optimal MTU size to ensure maximum network performance.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: User Experience That Successfully Improves Internet Speed by Setting MTU
A user, let’s call him Budi, experiences slow and often intermittent internet speeds, especially when streaming videos and playing online games. Budi uses a high-speed internet connection with a router that supports Ethernet networks.
Steps Taken
- Testing Internet Speed: Budi first tested internet speed using a speed testing site. The results showed a speed that was far below what it should be.
- Ping Test: Budi then conducts a Ping Test to determine the optimal MTU size. It uses the following command in the Command Prompt on a Windows computer:
ping google.com -f -l 1472
After several tests and packet size reduction, he found the maximum unfragmented packet size was 1464 bytes. By adding 28 bytes to the IP header, it determined that the optimal MTU size is 1492 bytes.
- Setting MTU on the Router: Budi then accesses the router settings and sets the MTU size to 1492 bytes in the WAN Settings section.
Result
After setting the optimal MTU size, Budi saw a significant increase in his internet speed. Video streaming runs smoothly without buffering, and the online gaming experience becomes more stable and responsive. The download and upload speed also increases according to the internet plan he uses.
Case Study 2: Cases of Failure Due to Suboptimal MTU Size and How to Overcome It
One user, let’s call him Ani, is having trouble with the VPN connection on his office network. When connected to a VPN, it often experiences long connection times and frequent disconnections. This problem has an impact on work productivity and access to company resources.
Problems Faced
- High Latency: Ani experiences high latency when connected to a VPN, which makes access to files and apps very slow.
- Packet Loss: There are significant indications of packet loss, which causes data to be frequently lost or corrupted during transmission.
Steps Taken
- Problem Identification: Ani consulted with the IT team in her office, who suspected the issue was related to suboptimal MTU sizing.
- Ping Test: The IT team performs a Ping Test to determine the optimal MTU size using the following command in Terminal on a macOS computer:
ping -D -s 1472 google.com
After several tests, they found that the maximum unfragmented packet size was 1432 bytes. By adding 28 bytes to the IP header, they determined that the optimal MTU size is 1460 bytes.
- Setting the MTU on the Router: The IT team then sets the MTU size to 1460 bytes on the office router and also sets it on the VPN configuration.
Result
After setting the optimal MTU size, the Ani VPN connection issue is resolved. Latency is significantly reduced, and there is no more significant packet loss. Access to files and apps through a VPN is faster and more stable, increasing Ani’s productivity at work.
Conclusion
Setting the optimal size of MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is essential to ensure maximum network performance and a stable internet connection. The main benefits of determining the right MTU size include Increasing Internet Speed, Reducing Latency and Packet Loss, and Improving Network Security and Network Stability and Reliability.
After determining the right MTU size, there are a few recommended steps to ensure network performance remains optimal. Perform periodic testing to ensure MTU size remains to meet your network needs. Network conditions can change over time, so it’s important to monitor and adjust the size of MTU if needed.


