Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) OSPF protocol is an interior routing protocol used to calculate the shortest path between routers within a single administrative domain (area). In OSPF, each router is responsible for calculating the routing table based on the network topology information and sending updates periodically.
OSPF was first defined in RFC 1131 in 1989. It replaces the RIP (Routing Information Protocol) protocol which has limitations at scale and slow convergence. OSPF has continued to undergo development and refinement since then, including support for IPv6 and security features.
OSPF allows routers to communicate and exchange information about network topology. Using the Dijkstra algorithm, OSPF calculates the shortest path (based on cost) between two points in the network. OSPF also supports area partitioning to manage large-scale networks.
Why Choose OSPF?
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a prevalent routing protocol with many advantages over protocols such as RIP and EIGRP. One of the main advantages of OSPF is its high scalability, which allows large networks to be divided into multiple areas, thus reducing the load on the router.
In addition, OSPF has fast convergence thanks to the link-state algorithm, which allows the network to remain stable despite changes in topology.
Security and stability are also important factors why many networks choose OSPF. With plaintext and MD5 authentication support, OSPF ensures that only legitimate routers can participate in routing exchanges.
Additionally, OSPF can detect failures quickly and provide traffic rerouting to alternate paths without significant disruption, ensuring network redundancy and reliability.
In the industry, OSPF is used by many large tech companies such as Google and Amazon to manage their complex networks. Educational institutions, telecommunications companies, and government and military organizations also rely on OSPF for their reliability, flexibility, and strong security.
The use of OSPF in these various scenarios shows that this protocol is not only efficient but also highly reliable in maintaining network stability and security.
How OSPF Works
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is an efficient and reliable routing protocol, that uses link-state algorithms to determine the shortest path in a network. The basic principle of the OSPF algorithm is that each router collects link status information from other routers to build a complete map of the network.
Dijkstra algorithm is then used to calculate the shortest path from one node to another, ensuring the data always goes through the most efficient route.
Process of Forming and Maintaining Routing Tables
The OSPF process begins with the exchange of Hello packets between neighboring routers to form a relationship called adjacency. Once adjacencies are formed, the router starts exchanging Link-State Advertisements (LSAs), which contain information about the status and cost of the link.
All received LSAs are stored in the Link-State Database (LSDB), which is a complete overview of the network topology. Each router uses this LSDB to run Dijkstra algorithms and build routing tables, which determine the shortest path to each destination in the network.
Concepts of Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) and Link-State Database (LSDB)
LSAs a messages used by routers to advertise their link status. The information in LSAs includes cost metrics and the status of each link connected to the router.
LSDB is a collection of all the LSAs received by the router, providing a complete view of the network topology. With LSDB, each router can calculate the shortest path using Dijkstra algorithms, ensuring efficient and reliable routing.
Areas and Autonomous Systems (AS) in OSPF
Area Divisions in OSPF and Their Functions
OSPF uses the concept of area division to manage large and complex networks. By dividing the network into multiple areas, OSPF reduces the load on the router and makes network management easier.
Each area has its topology, and routers in one area only know the full details of the topology of that area, while information about other areas is summarized for efficiency. This improves the scalability and performance of the network.
Backbone Area (Area 0) and Its Important Role
The backbone Area, also known as Area 0, is the core of the OSPF network. All other areas should be connected to Area 0, which serves as the main path for the exchange of routing information between different areas.
Area 0 ensures that data can flow smoothly and efficiently across the network, connecting all areas centrally.
Inter-Area Routing and Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) Concept
Inter-area routing enables communication between different areas in the OSPF network. The router located on the border between the two areas is called Area Border Router (ABR). ABR encapsulates routing information from one area and advertises it to another, thereby reducing the amount of routing information that needs to be exchanged.
An Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) is a router that connects an OSPF network with an outside network or other routing protocol. ASBR imports and exports routes between OSPF and external routing protocols, allowing for seamless integration between OSPF and other networks.
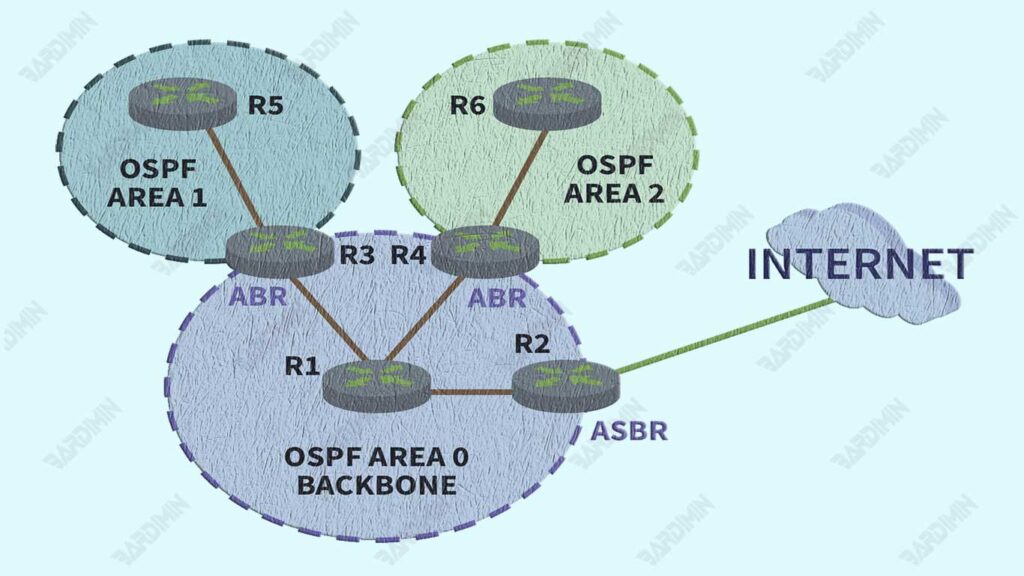
The figure above illustrates the division of areas in OSPF networks and the important role of Area 0. By understanding the concepts of areas and ASBR in OSPF, we can see how these protocols efficiently manage routing within large networks, ensuring optimal stability and performance.
Convergence and Path Recovery Methods
The convergence process in OSPF is the steps taken by the router to achieve a consistent state across the network after a topology change. Convergence begins with the exchange of Hello packets to establish adjacencies between neighboring routers.
Once adjacencies are formed, routers exchange Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) containing the latest information on the status and cost of the link. This information is used to update the Link-State Database (LSDB), and the Dijkstra algorithm is run to recalculate the shortest path to each destination. This process ensures that all routers have a consistent view of the network and can make efficient routing decisions.
Detection and Handling of Network Topology Changes
OSPF has an efficient mechanism for detecting and handling changes in network topology. Each router regularly sends Hello packets to its neighboring routers. If the router does not receive a Hello response within a certain time interval, it assumes that the link has gone down and immediately sends a new LSA reflecting the change in the status of the link.
These LSAs are then distributed to all routers in the area, and LSDB is updated. The algorithm Dijkstra reruns to calculate the new path, ensuring that traffic is immediately diverted to an available alternate path.
Fast and Efficient Path Recovery Mechanism
OSPF is designed to minimize path recovery time in the event of a link or router failure. Some of the recovery mechanisms used in OSPF include:
- Fast Reroute (FRR): This technique allows routers to immediately redirect traffic to alternate paths without waiting for full convergence, thereby reducing downtime.
- Loop-Free Alternate (LFA): This method ensures that the chosen alternate path does not form a loop, maintaining routing efficiency.
- Incremental SPF (iSPF): Instead of recalculating the entire path from scratch, iSPF only recalculating the part of the topology affected by the change, speeding up the convergence process.
OSPF Basic Configuration
Before starting OSPF configuration, it is important to ensure that the hardware and software that will be used are ready. Make sure the router has firmware or operating system that supports OSPF.
Also, make sure that all the devices are properly connected to the desired network topology. Update the firmware if necessary and make sure the physical connection and network interface are working properly.
OSPF Configuration Steps on a Router
- Enter Global Configuration Mode: Start by entering global configuration mode on the router.
- Enable OSPF Protocol: Configure OSPF by enabling this protocol and specifying the OSPF process ID.
- Assign Router ID: Each router in the OSPF network must have a unique Router ID.
- Configure OSPF Networks: Determine which networks will participate in the OSPF and specify the appropriate areas.
- Define OSPF Areas: Each network in OSPF should be assigned to a specific area, such as Area 0 for the backbone.
Example of OSPF Configuration Using CLI Commands
- Here is an example of a basic OSPF configuration on a Cisco router using CLI commands:
# Enter global configuration mode Router> enable Router# configure terminal # Enable OSPF and assign process ID Router(config)# router ospf 1 # Assign Router ID Router(config-router)# router-id 1.1.1.1 # Configure the OSPF network and define the area Router(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.25 area 0 Router(config-router)# network 10.0.000.0.0.0.25 area 1 # Exit router and global configuration mode Router(config-router)# exit Router(config)# exit Router# write memory
In the example above:
- The process ID OSPF is set as 1.
- Router ID is set as 1.1.1.1.
- Network 192.168.1.0/24 is set to Area 0.
- Network 10.0.0.0/24 is set to Area 1.
With these steps, you can configure OSPF on the router to ensure efficient and reliable routing in your network. Be sure to adjust the settings according to the topology and specific needs of your network.
OSPF Implementation Case Study
Case Studies in Large and Small Companies
Large Companies
A global technology company decided to implement OSPF in its network spread across different countries. Before implementation, they used RIP, which led to slow convergence and poor routing efficiency.
With OSPF, companies can divide the network into multiple areas, reduce the load on the router, and ensure the shortest path is calculated quickly. Fast convergence and Area Border Router (ABR) significantly improve network performance and stability.
Small Scale Companies
A startup company with two separate offices implemented OSPF to replace static routing. With OSPF, they can ensure that both offices have routing information that is always up-to-date and can adapt to topology changes automatically. This implementation helps them reduce downtime and increase the speed of data transfer between offices.
Implementation of OSPF on Campus Networks
A large university with several campus buildings spread over a large area implements OSPF to manage its network. Before OSPF, they had problems with routing efficiency and frequent downtime.
With OSPF, the university can divide the network into several areas, with Area 0 as the backbone that connects all buildings. OSPF ensures efficient and fast routing, reduces latency, and improves the user experience for staff and students.
Analysis of Implementation Results and Network Performance Improvement
After the implementation of OSPF, all case studies showed a significant improvement in network performance. Here are some of the results observed:
- Large Enterprises: Fast convergence and more efficient routing reduce latency and increase network throughput. Network stability is improved, with downtime drastically reduced.
- Small Scale Enterprises: Dynamic routing reduces the need for manual intervention in routing settings, saving IT time and resources. Connectivity between offices is more stable and fast.
- Campus Network: The use of the area within OSPF allows for more efficient network management. Reduced latency and increased data transfer speeds between buildings, providing a better experience for campus network users.
Conclusion
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a highly efficient and reliable dynamic routing protocol, ideal for networks of all sizes. Key benefits of OSPF include fast convergence, high scalability, and the ability to manage large networks through area partitioning.
By using the link-state algorithm, OSPF can quickly adjust to topology changes, ensuring optimal routing and minimizing downtime. Additionally, security features such as plaintext authentication and MD5 make OSPF a powerful choice for maintaining network integrity and reliability.
For readers considering implementing OSPF, it is important to understand your network topology and prepare supporting hardware and software. Start with the right division of areas and make sure Area 0 as the backbone is well connected. Perform OSPF configuration on the router carefully, making sure all steps are followed correctly.


