A computer network is a collection of hardware and software that allows computers to communicate with each other, and share data, and resources such as printers and internet connections.
Information flows through those networks, allowing network users to exchange documents and data with each other, print to the same printer, and generally share any hardware or software connected to the network. A node is a computer, printer, or other peripheral device connected to the network. A network can have tens, thousands, or even millions of nodes.
This network can be a local area network (LAN) that covers a limited area such as a single building, or a wider network (Wide Area Network / WAN) that covers a larger geographic area.

Using computer networks has many benefits, including improving work efficiency by allowing quick and easy access to data and resources. Computer networks also facilitate better communication between users in different locations, support team collaboration, and reduce operational costs through more efficient use of resources. In addition, the network enables the centralization of data, improves data security, and supports automatic data backup, which is critical for businesses and organizations.
Main Components of Computer Networks
Node
Nodes are basic components in a computer network that serve as a connecting point between other devices. Each node can be a computer, printer, server, or other device connected to the network. Nodes act as senders and receivers of data, allowing information to move through the network.
Node Roles:
- Data Sender: A node can send data to other nodes in the network.
- Data Receiver: Nodes can also receive data from other nodes.
- Data Flow Organizer: Nodes help organize the flow of data within the network, ensuring that data reaches its destination effectively.
Cabling
The commonly used types of network cables are Twisted-pair and Thin Coax.
Twisted-Pair (10BaseT):
- A twisted-pair cable consists of 8 wires connected in two pairs of twisted wires. These cables are relatively inexpensive and easy to install.
- Advantages: Inexpensive, flexible, and ideal for short distances.
- Disadvantages: Twisted-pair cables have a lower data transfer speed compared to other cables.
Thin Coax (10Base2):
- Thin coax cables are made of copper and have a larger diameter than twisted-pair cables. This cable is often used to connect the VCR to the TV.
- Advantages: Can be used for longer distances and has a higher data transfer speed.
- Disadvantages: More expensive and more difficult to install than twisted-pair cables.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
A NIC is a piece of hardware that allows a computer to connect to a network. The NIC serves as a link between the computer and the network, converting the data that will be transmitted through the network into electronic signals that can be understood by other network devices.
There are two types of NICs:
- Cable NICs that use a physical connection via Ethernet cable
- A wireless NIC that uses radio waves to connect to a Wi-Fi network.
Hub
A hub is a device used to gather multiple computers into a single network. The hub allows multiple computers to share resources and communicate with each other.
Types of Hubs:
- Hub Ethernet Standard (10Mbps): Used for standard Ethernet networks with a speed of 10Mbps.
- Hub Fast Ethernet (100Mbps): Used for Fast Ethernet networks with a speed of 100Mbps.
The Hub allows users to build larger networks with tens, hundreds, or even thousands of nodes.
Switch
A switch is a networking device that connects multiple computers in a local area network (LAN) and works smarter than a hub. The switch receives the data sent from one device and only forwards it to the destination device, thereby reducing the risk of collision and improving network efficiency.
Switches allow data to move more efficiently and effectively, as well as improve network speed and security.
Types of Switches
1. Switch Ethernet (Layer 2):
Ethernet switches operate on the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. They can filter and route data based on MAC (Media Access Control) addresses.
Advantages: Improves network speed and efficiency by reducing conflicts and disruptions.
Disadvantages: Cannot filter the top layer (Layer 3 and top), so it cannot distinguish between different data packets.
2. Switch Router (Layer 3):
Switch Routers operate on the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model. They can filter and route data based on IP addresses.
Advantages: Can filter the top layer, allowing users to differentiate between different data packages.
Disadvantages: More complex and expensive than Ethernet switches, thus requiring a deeper knowledge of internetworking.
3. Switch Gigabit Ethernet (1000BaseT):
Gigabit Ethernet switches operate at a speed of 1000 Mbps, which is faster than standard Ethernet switches.
Advantages: Increases network speeds up to 1000 Mbps, ideal for applications that require high speeds such as desktop and multimedia video.
Disadvantages: More expensive than standard Ethernet switches and require special equipment to connect them.
4. Switch Fiber Optic (1000BaseSX/LX):
Fiber Optic switches operate at a speed of 1000 Mbps using fiber optic technology.
Advantages: Increases network speeds up to 1000 Mbps and offers higher security because it does not use copper cables.
Disadvantages: More expensive than standard Ethernet switches and require special equipment to connect them.
Types of Network Topologies
Network topology is the physical or logical form of a computer network. This topology describes how devices in a network are interconnected with each other. Choosing the right topology is crucial because it will affect the network’s performance, reliability, and cost.
Here are some commonly used types of network topologies:
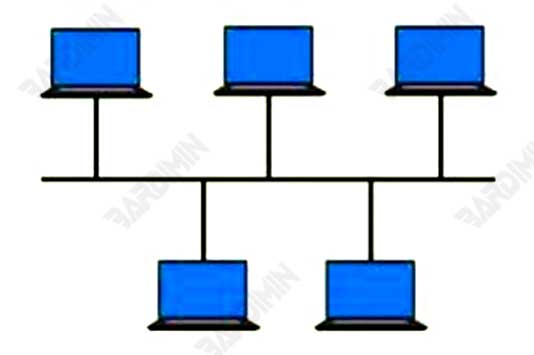
1. Bus Topology
Bus topology is one of the simplest types of network topology. In a bus topology, all network devices are connected to a main cable called a “backbone.” This cable serves as the main path to transmit data from one device to another. Each device has only one connection to the main cable and does not have a direct connection with other devices.
Pros: Easy to install and cheap.
Cons: If the main cable breaks, the entire network will be disrupted.
2. Star Topology
Star topology is the most commonly used type of network topology. In a star topology, each device is connected to a center called a “switch” or “hub.” Each device has a direct connection to the hub, and data is sent from the device to the hub and then to the other devices.
Pros: Easy to manage, if there is a problem device it will not interfere with the entire network.
Cons: If the hub or switch is damaged, the entire network will be disrupted.

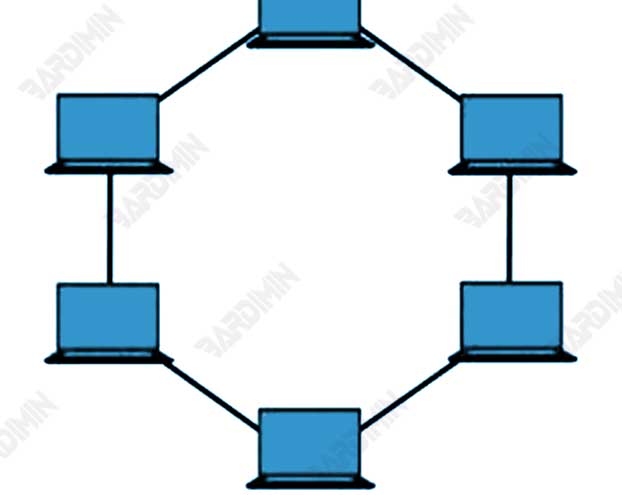
3. Ring Topology
Ring topology is a type of network topology that is more complex than bus topology. In a ring topology, each device is connected to the other in a chain, forming a circle. Data is transmitted from one device to another in a specific direction, and each device can only transmit data to the next device in a loop.
Pros: Data can flow in both directions.
Cons: If there is damage to a single device, the entire network can be disrupted.
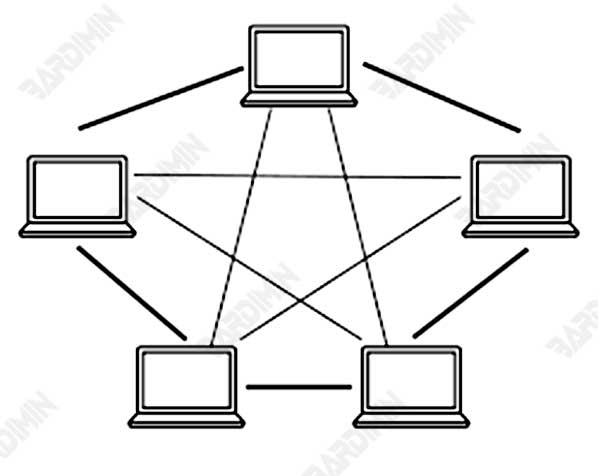
4. Mesh Topology
Mesh topology is the most complex and most fail-resistant type of network topology. In a mesh topology, each device is connected to every other device directly. Data can be transmitted through multiple paths, so if one path is damaged, the data can still move through the other.
Pros: Highly reliable because there are many alternative paths for data.
Cons: Requires a lot of cables and devices, making it very expensive.
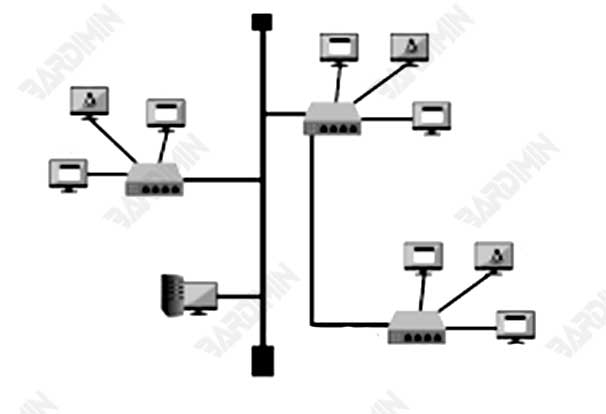
5. Tree Topology
A combination of bus and star topologies. It has a central device that connects to other devices in a hierarchical form, similar to tree branches.
Pros: Clear hierarchy, easy to manage.
Disadvantages: If the roots are damaged, all branches below them will be disturbed.
6. Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology is a combination of two or more basic network topologies, such as bus, ring, star, and mesh. The purpose of this topology is to combine the advantages of various topologies while reducing the disadvantages of each. Typically, hybrid topologies are used in large networks that require flexibility and scalability.
Pros: Flexible and can be adjusted to network needs.
Cons: Complexity in setup and management.
Ethernet Technology
Ethernet is a networking technology used to connect devices in a local area network (LAN). Known for its stability and ease of use, Ethernet has become the industry standard for wired networks. This technology regulates how data is sent and received over wires, as well as how devices in the network communicate with each other.
Types of Ethernet
1. Ethernet Standard (10Mbps):
- The speed is 10 Mbps, fast enough for most networking tasks.
- Ideal for small networks and applications that don’t require high speeds.
2. Fast Ethernet (100Mbps):
- Speed of 100 Mbps, faster than standard Ethernet.
- Ideal for networks that require high speeds such as desktop video and multimedia.
3. Gigabit Ethernet (1000BaseT):
- The speed of 1000 Mbps, is very fast and ideal for applications that require high speeds such as 4K video and other heavy applications.
4. Ethernet Fiber Optic (1000BaseSX/LX):
- Using fiber optic technology to improve network speed and security.
- Ideal for networks that require high speeds and higher security.
Types of Networks by Scale
Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that is limited to a relatively small area, such as an office, school, or apartment. LANs allow devices within the region to communicate and share resources.
Application:
- Office: LANs are widely used in offices to share files, printers, and applications.
- Schools: LANs help students and teachers share resources and information.
- Apartments: LANs allow apartment residents to share the internet and other resources.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers a wider area, such as a city, country, or even the world. WAN allows devices in different locations to communicate and share resources.
Application:
- Large Enterprises: WANs are used by large companies to connect branch offices in various locations.
- Government: The WAN assists the government in managing information and resources across various departments.
- Internet Services: WANs are used by Internet service providers to provide Internet access to customers around the world.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a network that covers metropolitan areas, such as large cities. MAN enables devices within the metropolitan area to communicate and share resources.
Application:
- Big Cities: MAN is used by big cities to connect public facilities such as train stations, shopping malls, and healthcare facilities.
- Education: MAN assists educational institutions in managing information and resources across various campuses.
- Large Corporations: MAN is used by large companies to connect offices within large cities.
Network Model
Peer-to-Peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) is a networking model in which each device functions as a client and server simultaneously. Each device can send and receive data, as well as share resources with other devices.
Excess:
- Simple: P2P installation and use is relatively simple as it does not require a central server.
- Easy Sharing: P2P allows users to share files and resources easily.
- No Server Required: There is no need to have an expensive and complex central server.
Deficiency:
- Capacity Limitations: P2P has capacity limitations because each device has to share bandwidth simultaneously.
- Interference: If one of the devices fails, then the entire network will be disrupted.
- Security: P2P is vulnerable to cyberattacks because data can move freely between devices.
Client-Server
Client-server is a network model in which each device functions as a client accessing resources from a central server. Servers store and manage resources, while clients access and use those resources.
Excess:
- Stable Performance: Client-server provides stable performance as data does not need to share bandwidth simultaneously.
- Fail Resistant: If one of the clients fails, then the data is still accessible through the server.
- Security: Client servers are more secure because data is stored and managed by servers that have tighter controls.
Deficiency:
- Complex: Client-server installation and deployment are more complex because they require expensive and complex central servers.
- High Cost: It costs a lot to buy and maintain a central server.
- Server Dependency: The network depends on the performance of the server, so if the server fails, then the entire network will be disrupted.
Conclusion
Computer networks play a crucial role in connecting devices and enabling communication and resource sharing. The selection of the right topology, technology, network type, and network model depends largely on the specific needs and scale of the desired network. By understanding these various aspects, we can design and manage an efficient, secure, and reliable network.


