Windows 11 offers a variety of advanced features to improve user productivity and security. One important thing that is often overlooked is the understanding of Local Profile and Roaming Profile. Both types of profiles have an important role in data storage and access, as well as user settings.
Choosing the right profile affects work efficiency and data security. For example, a Local Profile is more suitable for users who only use one device, while a Roaming Profile is ideal for those who switch devices or locations frequently.
In this article, Bardimin will provide a complete guide regarding the differences, benefits, and how to choose between Local Profile and Roaming Profile in Windows 11. By understanding these two options, you can maximize the use of the operating system according to your personal or professional needs.

What Are User Profiles in Windows 11?
In Windows 11, a user profile is a set of settings, files, and preferences that are unique to each user. These profiles allow everyone who uses the same computer to have an experience that suits their needs and desires without disturbing other users. Each user profile has a separate account, which increases security, maintains privacy, and protects important data.
User profiles have several important benefits:
- Allows each user to set up their desktop, apps, and settings to their liking.
- Keep each user’s files and documents separate and organized, preventing unwanted access by other users.
- Each user account has different access rights (Administrator or Standard User), which provides greater control over system changes and software installations.
- With a Microsoft account, settings and preferences can be synced across multiple devices, providing a uniform experience.
By default, the user profile file is stored in the C:\Users\<Username> directory. This folder contains sub-folders such as Desktop, Documents, Downloads, Pictures, and more, which store the user’s files and data. Understanding the structure of these folders is important for troubleshooting, data backup, and user profile management. By knowing this location, users can easily back up important data or recover deleted profiles.
Getting to know Local Profiles in Windows 11
A local profile is a type of user profile in Windows 11 that is stored on the device itself. This means that all user data, such as documents, settings, and preferences, are only available on those devices. This profile is ideal for users who only use one device and don’t need to access data from another location or device.
When you sign in to Windows 11 with a Local Profile, the system will load all the settings and files that are in the C:Users<Username> folder. This data is not synced with the cloud or server, so it can only be accessed from that device. Any changes you make, such as changing the desktop theme or saving a new file, will only take effect on the local device.
Advantages of Local Profiles
1. Faster Access
Because data is stored locally, access to files and settings becomes faster without depending on network or internet speed.
2. Safer for Personal Use
Local Profile is ideal for users who prioritize privacy and security, especially if the device is not always connected to the internet.
3. No Connection to Server Required
You can log in to the system and access your data at any time without needing to connect to an external server or network.
Disadvantages of Local Profiles
1. Not Accessible from Other Devices
The data on the Local Profile can only be accessed on that device. If you need to access the data from another device, you will have to move the files manually.
2. Risk of Data Loss
If your device is damaged, lost, or infected with malware, the data in the Local Profile can be lost unless you have made a separate backup.
Understanding Roaming Profiles in Windows 11
A Roaming Profile is a type of user profile in Windows 11 that is stored on a network server instead of on a local computer. It allows users to access their data and settings from various devices connected to the same network. With Roaming Profiles, the user experience remains the same, no matter what device is used.
How Roaming Profiles Work
Whenever a user logs in to Windows 11 with a Roaming Profile, the system will download the profile data from the server to the device being used. Once the session is complete, all changes made (such as new files or changed settings) will be uploaded back to the server. This process ensures that the data is always up-to-date and accessible from other devices.
Advantages of Roaming Profiles
1. Consistent User Experience
Users can work on different devices with the same settings and files, so the experience remains uniform.
2. Data Security
Since the data is stored on the server, the risk of data loss due to damage or loss of the device can be minimized.
3. Ideal for Multi-Device Environments
It is suitable for users who often switch devices, such as employees who work in the office and home or students who use laptops and computers in the laboratory.
Disadvantages of Roaming Profiles
1. Requires a Stable Network Connection
Roaming Profiles relies on a network connection to download and upload data. If the network is slow or unstable, users may have trouble signing in or syncing.
2. Longer Login Time
The login process can take longer because the system needs to download profile data from the server.
3. Risk of Profile Damage
If there is a problem during the sync process (for example, the network is down), the user profile could be corrupted, which can cause problems when signing in later on.
Comparison of Local vs. Roaming Profile in Windows 11
Here is a comparison between the Local Profile and the Roaming Profile based on various important aspects:
| Aspects | Local Profile | Roaming Profile |
| Storage Location | On the local device (C:\Users<Username>) | On the network server (\ServerName\Profiles<Username>) |
| Accessibility | Only available on one device | It can be accessed from other devices in the network |
| Login Speed | Fast, as it doesn’t require network synchronization | It can be slower because it has to download data from the server |
| Data Security | Prone to data loss if the device is damaged or exposed to viruses | More secure because data is stored on the server and can be recovered |
| User Mobility | It cannot be used on other devices | Allows users to switch devices with the same experience |
| Network Connection Needs | No network connection is required | Requires a stable network connection |
| Risk of Corruption Data | Low, as all data is only stored locally | There is a risk of data corruption if synchronization with the server fails. |
| Suitable For | Individual users using only one device | Business, enterprise, or organization environments with multiple devices |
| Other Advantages | A place to collect all the user’s programs and files. Changes are limited to that profile only. A consistent environment for every login on the same computer. | Users have a consistent experience. Files are available on a variety of computers. Younger computer replacement/backup. |
| Loss | It cannot be transferred to another computer. Inefficient when you need more than one local profile on the PC. Can’t install paid apps from the Microsoft App Store. | Increased network traffic and login time. The more files you have, the longer the download time will be. Relatively outdated technology. Profiles may be corrupted in the event of sync issues. |
It’s important to note that Roaming Profiles may require additional configuration, such as installing Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) in Windows 10 and configuring Group Policy Objects (GPO) in Active Directory to direct user profiles to network shares appropriately.
In addition, there are special considerations to enable the roaming Start menu and address potential issues with operating system upgrades. While Roaming Profiles offer many advantages in a corporate environment, it is important to consider the potential for increased network traffic and longer login times.
How to Switch from Local Profile to Roaming Profile in Windows 11
To switch from Local Profile to Roaming Profile in Windows 11, you need to follow some technical steps, especially if you’re on a network that uses Active Directory (AD). Here is a step-by-step guide to making this change:
Step 1: Ensure Access to Active Directory (AD) and Group Policy Management
Make sure you have administrative access rights to Active Directory and Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). This is required to configure the Roaming Profile at the network level.
Step 2: Log in to Control Panel > System > Advanced System Settings
- Open Control Panel.
- Select System and Security > System.
- In the left panel, click Advanced system settings.
- In the window that appears, select the Advanced tab.
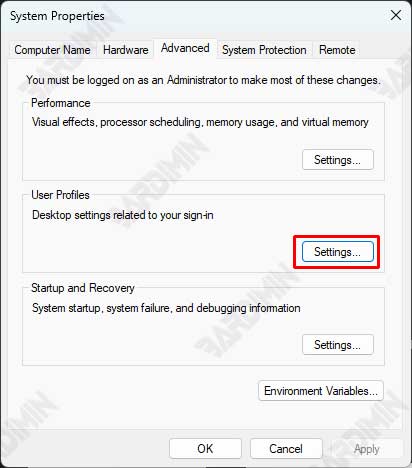
Step 3: Select Tab User Profiles and Change Profile Type
- Under the User Profiles section, click the Settings button.
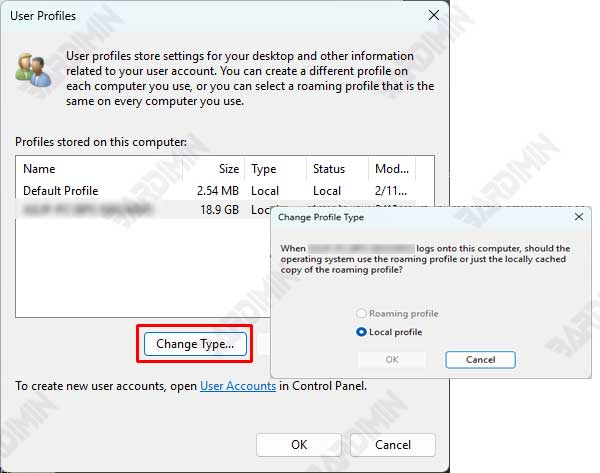
- In the User Profiles window, select the user profile you want to change from Local to Roaming.
- Click Change Type.
- Select the Roaming Profile option and click OK.
Step 4: Configure Roaming Profile Path in Group Policy Editor
- Open Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) by typing gpmc.msc in the Start menu and pressing Enter.
- Navigate to Group Policy Object (GPO) associated with your user or computer.
- Right-click on the GPO and select Edit.
- In Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to:
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > System > User Profiles- Find and enable the Set roaming profile path for all users logging onto this computer policy.
- Enter the path of the server where the roaming profile will be stored, for example:
\\ServerName\Profiles\%Username%- Save the changes and close Group Policy Management Editor.
Step 5: Restart the Computer and Test Sync
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
- After restarting, log in to the user account that has been changed to Roaming Profile.
- Test syncing by making changes to settings or files, then signing in from another device to make sure those changes are synced.
Choosing between Local Profile and Roaming Profile in Windows 11 is a decision that needs to be tailored to your needs and work environment. Local Profiles are suitable for individual use that relies on only one device, such as designers or authors, because they offer high access speeds and local data security.
On the other hand, Roaming Profile is ideal for business environments or users who switch devices frequently, as it allows data access from various locations and devices with maintained consistency. The selection of these profiles depends on three main factors: accessibility, security, and speed.
If you need flexibility and data synchronization between devices, Roaming Profile is the best option. However, if you prioritize the speed and security of locally stored data, Local Profiles are a better fit. By understanding the differences and benefits of each, you can optimize the use of Windows 11 according to your personal or professional needs.


