VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a programming language in Microsoft Office applications, such as Excel, Word, and PowerPoint. Using VBA, users can automate various tasks, improve efficiency, and create a more interactive experience. One of the important things in using VBA is its ability to communicate with users, whether to provide information, ask for input, or confirm actions before running the program.
The two main features that support this interaction are the Message Box (MsgBox) and the Input Box (InputBox). MsgBox serves to display messages or request confirmation from users, while InputBox allows users to enter data to be used in VBA code. Both are particularly useful in a variety of situations, such as displaying warnings before deleting data, asking users to enter numbers in automated calculations, or displaying reports of results from macro processes.
For example, in an Excel application, a data analyst can leverage MsgBox to provide warnings before running macros that delete important data. On the other hand, InputBox can be used to ask users to enter certain parameters, such as the month or year of the report to be processed. By understanding and optimizing the use of MsgBox and InputBox, VBA users can improve program interactivity and ensure more secure and controlled macro execution.
Getting to know the Message Box in VBA
Message Box (MsgBox) is a feature in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) that is used to display messages to users in the form of pop-up dialogs. MsgBox is often used to provide information, display alerts, ask for confirmation before running a process, or notify the outcome of a command in a macro.
When a MsgBox is displayed, the user must press one of the available buttons before the program can continue its execution. Depending on the needs, MsgBox can be configured with a variety of button and icon combinations to improve the effectiveness of communication within VBA applications.
Basic Syntax of MsgBox
The basic syntax for displaying Message Box in VBA is as follows:
MsgBox “This is a message from VBA!”The code above will display a pop-up window with the text “This is a message from VBA!” and one button OK to close the message.
Button Types in MsgBox
MsgBox can be configured with a variety of buttons to provide interaction options to users. Here are some commonly used button types:
| Constant | Description |
| vbOKOnly | Displays only the OK button (default). |
| vbOKCancel | Displays OK and Cancel buttons. |
| vbYesNo | Displays Yes and No buttons. |
| vbRetryCancel | Displays Retry and Cancel buttons. |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | Displays Abort, Retry, and Ignore buttons. |
Examples of using MsgBox with various buttons:
MsgBox “Do you want to continue?”, vbYesNo, “Confirm”The code above will show a MsgBox with the Yes and No buttons, as well as the “Confirm” title on the pop-up.
Adding Icons to MsgBox
In addition to the buttons, MsgBox can also display icons to clarify the type of message being given. Here are some icons that can be used:
| Constant | Displayed Icons |
| vbCritical | Warning icon (❌) |
| vbQuestion | Question mark icon (❓) |
| vbExclamation | Fun icon (⚠️) |
| vbInformation | Information icon (i️) |
Examples of icon usage in MsgBox:
MsgBox “Data entered is invalid!”, vbExclamation, “Warning”This code will display MsgBox with an exclamation mark icon (⚠️) to signal a warning to the user.
Capturing User Responses with MsgBox using If… Else
In some cases, we need to capture the user’s preferences from MsgBox to determine the next step in the VBA code. This can be done by storing MsgBox results into variables and using If…Else to process user responses.
Examples of using MsgBox to capture user responses:
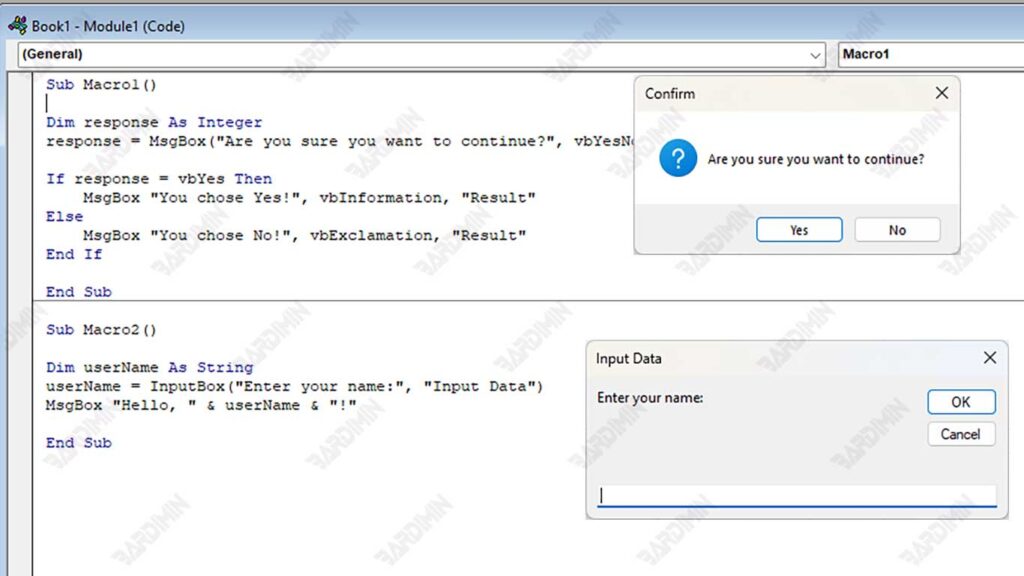
Dim response As Integer
response = MsgBox(“Are you sure you want to continue?”, vbYesNo + vbQuestion, “Confirm”)
If response = vbYes Then
MsgBox “You chose Yes!”, vbInformation, “Result”
Else
MsgBox “You chose No!”, vbExclamation, “Result”
End IfGetting to Know the Input Box in VBA
Input Box (InputBox) is a feature in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) that allows users to enter data in the form of text or numbers through a simple dialog window. InputBox is often used to request information from users, such as names, numbers, dates, or other data required in VBA processing.
Basic Syntax of InputBox
The basic syntax for displaying InputBox in VBA is as follows:
Dim userName As String
userName = InputBox(“Enter your name:”, “Input Data”)
MsgBox “Hello, “ & userName & “!”Code explanation:
- InputBox will display a dialog with the text “Enter your name:”.
- The data that the user types will be stored in the userName variable.
- MsgBox will display the greeting “Hello, [name inputd]!” after the user presses OK.
Specifying the Default Value in the InputBox
You can set the default value in InputBox to provide an example of the expected input.
Example code with default values:
Dim city As String
city = InputBox(“Enter your city name:”“, “Input Data”, “Jakarta”)
MsgBox “You live in “ & city & “!”Explanation:
- “Jakarta” will appear as the default text in the InputBox.
- Users can edit or directly press OK to use the default value.
Input Validation from the InputBox to Ensure the Input Data is Correct
Since InputBox only receives input in the form of text, it is important to validate that the data entered is as expected.
Example of validation of inputs so that they are not empty:
Dim userInput As String
userInput = InputBox(“Enter your email:”, “Input Email”)
If userInput = ““ Then
MsgBox “Input cannot be empty!”, vbExclamation, “Warning”
Else
MsgBox “The email you entered: “ & userInput, vbInformation, “Confirmation”
End IfExplanation:
- If the user presses OK without filling in the data, a warning will appear.
- If there is a valid input, a confirmation will appear with the entered data.
An example of input validation only accepts numbers:
Dim age As String
age = InputBox(“Enter your age:”, “Input Age”)
If IsNumeric(age) Then
MsgBox “Your age is “ & age & “ years.”, vbInformation, “Confirm”
Else
MsgBox “Please enter a valid number!”, vbCritical, “Error”
End IfExplanation:
- IsNumeric() is used to check whether the input is a number.
- If it is not a number, an error warning will appear.
Comparing MsgBox and InputBox: When to Use It?
In VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), both Message Box (MsgBox) and Input Box (InputBox) are used to interact with users, but they have differences in their functions and how they are used. MsgBox focuses more on providing information and getting responses in the form of button choices, while InputBox is used to ask for input directly from users.
Here is a comparison between MsgBox and InputBox based on their key features:
| Feature | Message Box (MsgBox) | Input Box (InputBox) |
| Main functions | Display messages and get a response (Yes/No/Cancel) | Requesting input from users (text/numbers) |
| User interaction | Limited to available buttons | Can accept text or number input |
| Customization | You can add icons and titles | Can display default values |
| Usage examples | Notifications, alerts, action confirmation | Data input form, search, validation |
When to Use MsgBox?
Use MsgBox when you want to:
- Displays alerts or information to users.
- Ask for action confirmation before running the process.
- Provides a choice between Yes/No, OK/Cancel, or other buttons.
When to Use InputBox?
Use InputBox when you want to:
- Asks users to enter text, numbers, or other necessary data.
- Use user input as a parameter in the VBA process.
- Allows users to fill out forms or perform searches.


