Do you often work with multiple Excel files and need to combine them into one complete document? The process of merging Excel files has become an essential need for professionals handling monthly reports, regional sales data, or financial data consolidation. With the right method, this task can be completed quickly and efficiently.
As a professional, you might face situations where you need to combine daily reports into a monthly report. Or perhaps you need to consolidate sales data from various regions into one centralized file. This process of merging Excel files can present its own challenges, especially when the number of files to merge is considerable.
There are actually several methods to perform merging Excel files. For a small number of files, you can use manual methods like copy-paste or the Move/Copy Sheet feature. However, manual methods are time-consuming and prone to errors. Therefore, for time efficiency and data accuracy, using VBA Macro becomes the best solution.
Advantages of Using VBA Macro for Merging Excel Files
VBA Macro offers several significant advantages in the data consolidation process. First, the automated process drastically saves time. Second, it reduces the risk of human error that often occurs with manual methods. Third, you can customize the script according to specific needs.
Steps to Merge Excel Files with VBA
- Open a new Excel file as the consolidation location
- Press the Alt + F11 key combination to open Visual Basic Editor
- In the VBA Editor window, click ThisWorkbook > Insert > Module
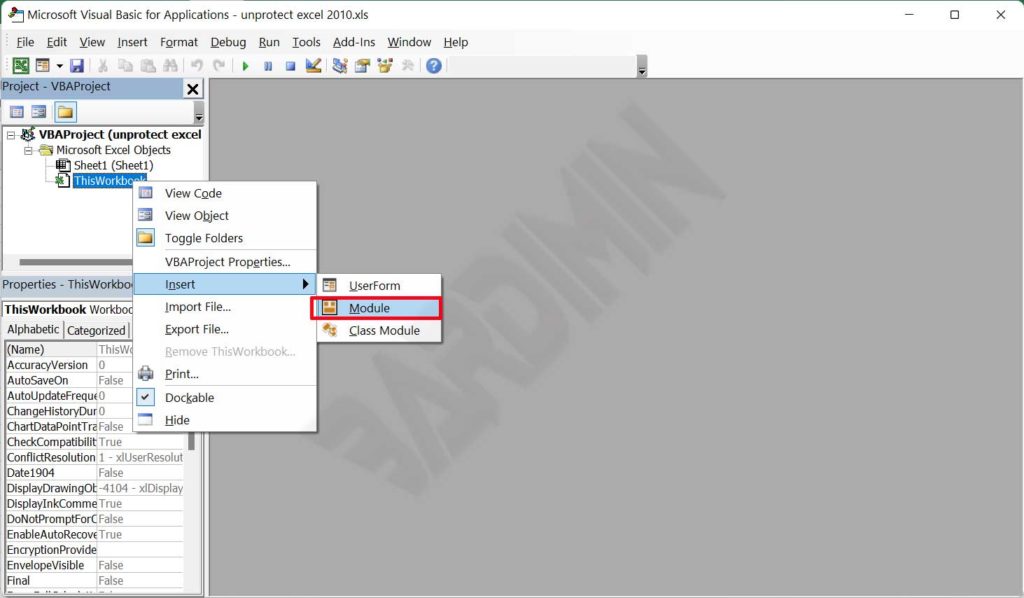
- Copy the following VBA script into the module
Sub MergeExcelFiles()
Dim fnameList, fnameCurFile As Variant
Dim countFiles, countSheets As Integer
Dim wksCurSheet As Worksheet
Dim wbkCurBook, wbkSrcBook As Workbook
fnameList = Application.GetOpenFilename(FileFilter:="Microsoft Excel Workbooks (*.xls;*.xlsx;*.xlsm),*.xls;*.xlsx;*.xlsm", Title:="Choose Excel files to merge", MultiSelect:=True)
If (vbBoolean <> VarType(fnameList)) Then
If (UBound(fnameList) > 0) Then
countFiles = 0
countSheets = 0
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationManual
Set wbkCurBook = ActiveWorkbook
For Each fnameCurFile In fnameList
countFiles = countFiles + 1
Set wbkSrcBook = Workbooks.Open(Filename:=fnameCurFile)
For Each wksCurSheet In wbkSrcBook.Sheets
countSheets = countSheets + 1
wksCurSheet.Copy after:=wbkCurBook.Sheets(wbkCurBook.Sheets.Count)
Next
wbkSrcBook.Close SaveChanges:=False
Next
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic
MsgBox "Processed " & countFiles & " files" & vbCrLf & "Merged " & countSheets & " worksheets", Title:="Merge Excel files"
End If
Else
MsgBox "No files selected", Title:="Merge Excel files"
End If
End SubSource: Ablebits.com
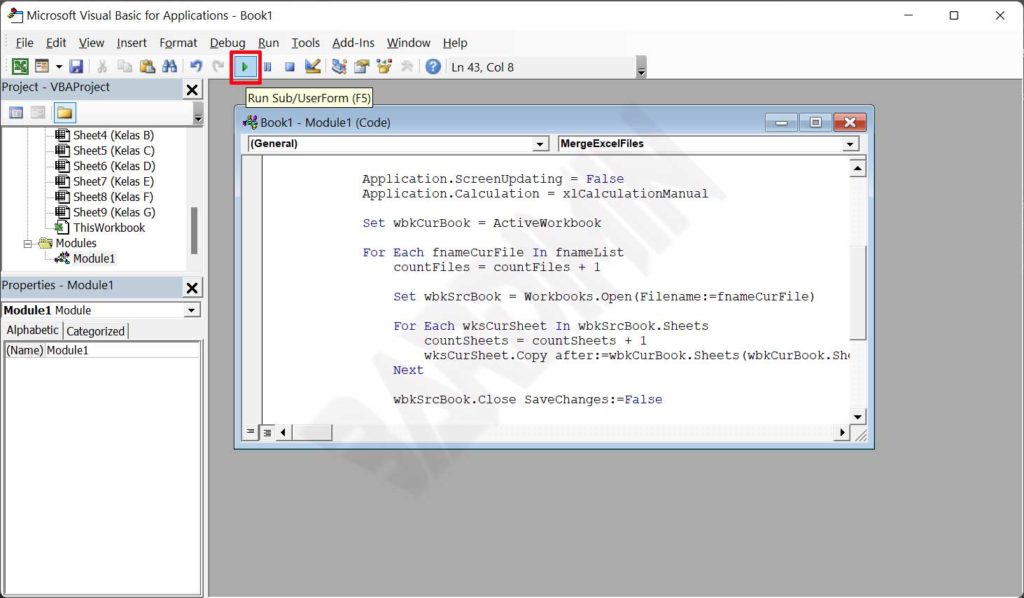
- Click the Run button or press F5 to execute the macro
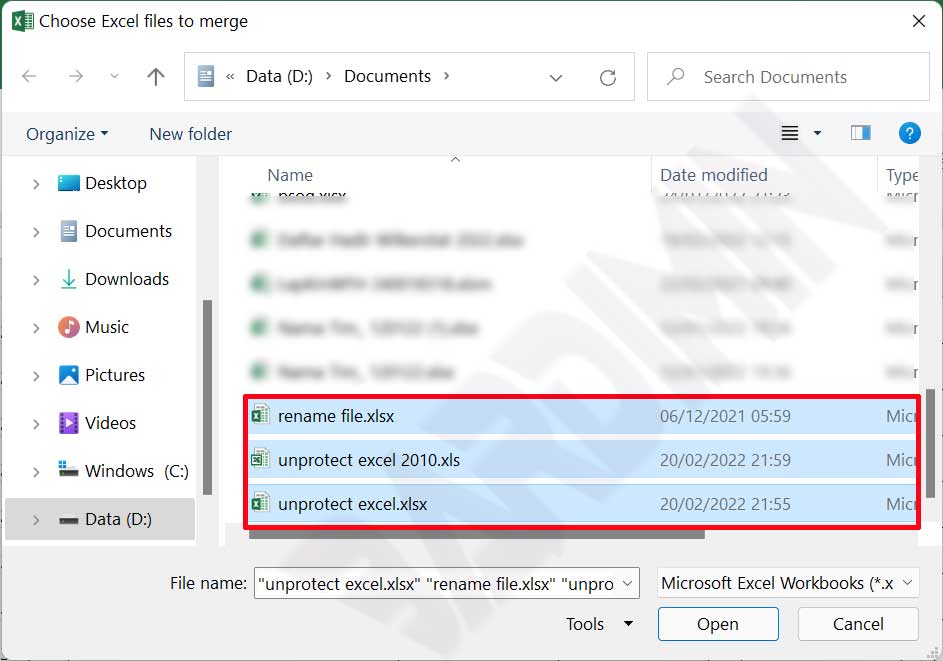
- Select all Excel files you want to merge, then click Open
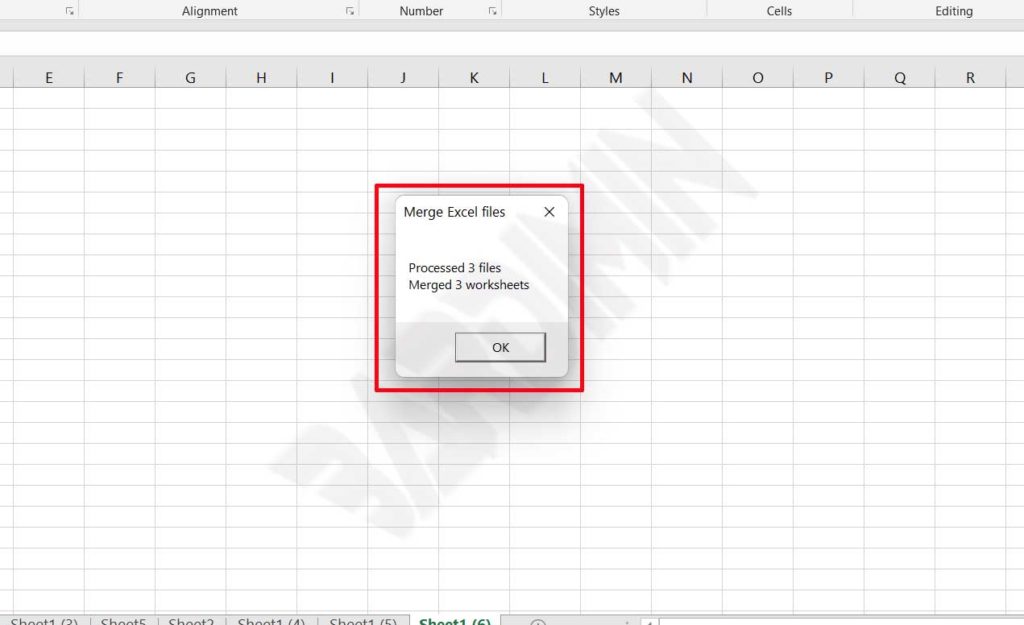
- Wait for the process until completion notification appears
Additional Tips for Merging Excel Files Process
Before running the merging Excel files process, ensure all files to be merged are closed. Additionally, backup important data first to anticipate unexpected issues. This process also requires enabling macros in Excel, so make sure the macro security settings are appropriate.
By following this guide, the process of merging Excel files can be done quickly and accurately. This VBA method is very effective for handling large-scale data consolidation, thereby significantly increasing your work productivity.


