If you’ve ever opened a computer case, you may see a small, round-shaped battery that resembles a watch battery. These batteries are located in the motherboard and are called CMOS batteries.
The motherboard is the main component in a computer that serves as a link between various hardware. The motherboard organizes the communication between the CPU (Central Processing Unit), RAM (Random Access Memory), GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), and other hardware.
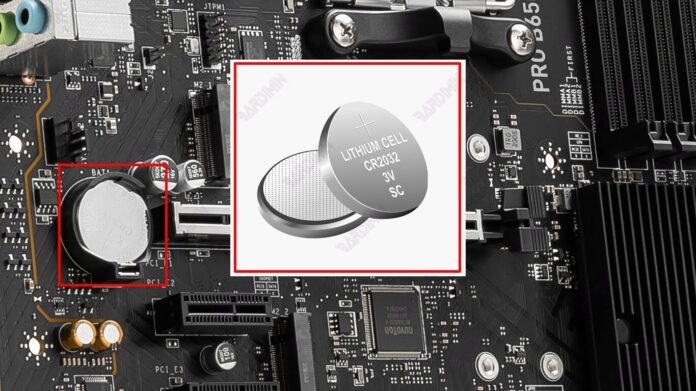
Coin batteries, often known as CR2032, are small, round, coin-shaped batteries located on the motherboard. Despite its small size, these batteries have a very vital role in keeping some basic computer functions running properly. In this article, we will explore why these coin batteries exist in motherboards and what they do.
Let’s explore why motherboards need these batteries and how their functions affect your PC’s performance.
What is a Coin Battery on a Motherboard?
Coin batteries, the most commonly used in motherboards, are lithium batteries known by the code CR2032. These batteries have a round and flat shape, similar to a coin, with a diameter of about 20 mm and a thickness of about 3.2 mm. CR2032 is one of the most popular types of batteries due to its large enough capacity for such a small size, as well as its long durability.
Coin batteries are usually installed in a special slot on the motherboard called a battery socket. This socket is designed to hold the battery securely and ensure good contact with the connector pins on the motherboard. Coin batteries are often located near the chipset or in an area that does not interfere with other components, making them easy to reach when they need to be replaced.
Main Functions of Coin Batteries on Motherboards
Maintaining Time and Date
One of the main functions of a coin battery on a motherboard is to keep the time and date settings on the computer. When the computer is turned off and not connected to a power source, this coin battery provides the power necessary to keep the internal clock and calendar running.
This is important because many applications and operating systems rely on accurate times and dates to function properly. If the time and date don’t match, you may face a variety of issues, from difficulty accessing websites to problems with file syncing.
Example: If you use a computer for business purposes, especially for scheduling, email, and applications that require accurate time, having the right time and date settings is always very important. Without a coin battery, every time your computer is turned off, you will have to manually reset the time and date when you turn it back on.
Saving BIOS/UEFI Settings
In addition to maintaining the time and date settings, coin batteries also have a crucial role in storing BIOS/UEFI settings. The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the firmware that governs the basic functions of your computer’s hardware. The BIOS/UEFI stores various important settings, such as boot order, hardware configuration, overclocking settings, and so on.
When the computer is turned off, the coin battery ensures that all of these settings remain stored and not lost. Without a coin battery, every time the computer is turned on, the BIOS/UEFI settings will revert to the factory default settings, which can cause various operational problems. For example, the boot order may change, and the computer may not be able to find the operating system correctly.
Example: If you have set the BIOS to boot from an SSD and not from an HDD, losing this setting will cause the computer to try to boot from the HDD by default, which may not have an operating system installed. This will cause the computer to fail to boot until you reset the BIOS.
Why are coin batteries so important?
Impact If Coin Battery Runs Out or Doesn’t Work
When the coin battery on the motherboard runs out or doesn’t work, your computer will experience various problems that can interfere with daily operations. Here are some of the impacts that can occur:
- Reset Time and Date Settings: Each time the computer is turned on, the time and date will revert to their default settings (usually January 1, 1970, or the start date of the BIOS). This can lead to problems with the software that requires accurate timing.
- BIOS/UEFI Reset: The BIOS/UEFI settings will revert to factory defaults whenever the computer is turned off, causing the hardware configuration to not be as desired.
- Boot Difficulty: With the BIOS settings reset, the computer may not be able to find the correct boot device, causing boot issues.
- Network and Security Issues: Inaccurate times and dates can cause problems in network authentication and security certificates, as many security systems rely on the right time for validation.
How the Computer Resets BIOS Time and Settings If the Battery Runs Out
When the coin battery is discharged, the motherboard loses the power needed to store the BIOS/UEFI settings and the time when the computer is turned off. Consequently:
- Time and Date Settings: The BIOS cannot maintain accurate time and date. Each time the computer is turned on, the BIOS will reset the time and date to the default values, usually the factory date or the year 1970.
- BIOS/UEFI Settings: All BIOS/UEFI configurations that have been customized by the user, such as boot sequence, overclocking settings, RAID configurations, etc., will be lost and returned to factory settings. This can cause the device to not work as expected, and in some cases, the computer may not boot properly.
A Real Example of a Problem Arising from a Depleted Coin Battery
- Boot Failure: A user reported that every time their computer was shut down, the boot order changed and the computer could not find the operating system. After investigation, it was found that the coin battery on the motherboard was dead. Each time the computer is shut down, the BIOS settings are reset, resulting in the boot order returning to default, which does not match the existing operating system configuration.
- Network and Security Issues: A network administrator finds that computers on his network often experience authentication and certificate validation issues. After some investigation, it was discovered that many computers had inaccurate timing due to the coin battery being depleted. Inaccurate timing causes security certificates to be considered invalid, thus preventing access to some network services.
- User Inconvenience: A user complained that every time their computer was turned on, they had to manually reset the time and date. This is a hassle especially because some apps like calendars, emails, and certain software rely on accurate timing. Upon inspection, it was found that the coin battery had run out and needed to be replaced.
How Long Do Coin Batteries Last?
Factors Affecting Coin Battery Life
The battery life of a coin on a motherboard can be affected by several factors, including:
- Battery Quality: Batteries from well-known brands such as Duracell, Panasonic, or Energizer usually have better quality and a longer lifespan than unbranded or low-cost brand batteries.
- Ambient Temperature: Coin batteries installed in environments with extreme temperatures (too hot or too cold) tend to experience a faster degradation in performance and lifespan.
- Computer Usage: The frequency of computer use also affects battery life. A computer that is turned off and turned on frequently will drain battery power faster than a computer that is turned off infrequently.
- Motherboard Quality: Some motherboards may have larger power leakage, which can drain the coin battery faster.
- BIOS/UEFI settings: Certain settings on the BIOS/UEFI that require more power can also speed up the drain of the coin battery.
Average Coin Battery Life and How to Know When It’s Time to Replace
The average battery life of a coin on a motherboard is about 3 to 5 years. However, this lifespan can vary depending on the factors mentioned above.
How to Replace a Coin Battery
Replacing the coin battery on the motherboard is a fairly easy task and can be done on your own. Here are the steps that can be followed:
- Turn off and unplug the computer: Make sure the computer is turned off and not connected to a power source.
- Open the Computer Case: Remove the computer case cover to access the inside of the motherboard.
- Find Coin Batteries: Look for coin batteries that are usually near the bottom or center of the motherboard.
- Remove Old Batteries: Carefully, use a small tool such as a flathead screwdriver to remove the battery from its slot.
- Install New Batteries: Insert a new coin battery into the slot paying attention to its polarity. Make sure the batteries are properly installed and that the contacts are perfect.
- Reinstall the Case: Once the battery is installed, close the computer case again and connect the power cable.
Differences between Different Types of Coin Batteries Commonly Used in Motherboards
The most commonly used coin battery in motherboards is the CR2032 type. However, there are several other types that you may encounter, each with different technical specifications. Here are some common types of coin batteries used in motherboards and their differences:
1. CR2032
- Voltage: 3V
- Capacity: 220 mAh
- Diameter: 20 mm
- Depth: 3.2 mm
- Usage: This is the most common type used in motherboards due to its adequate capacity and standardized size.
2. CR2025
- Voltage: 3V
- Capacity: 170 mAh
- Diameter: 20 mm
- Thickness: 2.5 mm
- Usage: Similar to CR2032 but has a lower capacity and is slightly thinner. It can be used as a temporary substitute, but it is not recommended for the long term.
3. CR2016
- Voltage: 3V
- Capacity: 90 mAh
- Diameter: 20 mm
- Thickness: 1.6 mm
- Usage: Much thinner and has a lower capacity than CR2032. Not recommended for use in motherboards due to its shorter durability.
Choosing the Right Coin Battery
A Guide to Choosing the Right Coin Battery for Your Motherboard
- Check Motherboard Specifications
- Before purchasing a replacement coin battery, be sure to check your motherboard’s manual or documentation. Look for information about the recommended coin battery type and size.
- Make Sure the Voltage Is the Same
- Generally, motherboards use coin batteries with a voltage of 3V, such as CR2032. Make sure the replacement battery has the same voltage to avoid damage to the motherboard.
- Pay attention to the battery capacity
- Battery capacity is measured in milliampere-hours (mAh). For motherboard purposes, choose a battery with adequate capacity. The CR2032 battery typically has a capacity of around 220 mAh, which is ideal for maintaining timing and BIOS.
- Suitable Size
- The diameter and thickness of the coin battery are very important. CR2032 has a diameter of 20 mm and a thickness of 3.2 mm. Make sure the replacement battery is the same size to fit in the motherboard slot.
- Choose a Trusted Brand
- The quality of coin batteries is essential for longevity and performance. Choose batteries from reputable brands that have a good reputation for quality products.
- Check Production Date
- Newer batteries have a longer lifespan. Be sure to check the manufacturing date on the battery pack to make sure you are getting a new and fresh battery.
- Buy from Trusted Sources
- To avoid counterfeit or low-quality products, buy batteries from trusted retailers, both physical and online stores that are reputable.
Recommended and Best Coin Battery Brands on the Market
Here are some recommended coin battery brands that are known to be of good quality:
- Duracell CR2032
- Pros: Duracell is known for its long durability and consistent quality. These batteries are often recommended for a variety of applications including motherboards.
- Reputation: One of the best battery brands in the world with many positive reviews from users.
- Energizer CR2032
- Pros: Energizer offers a battery with long durability and stable performance. These batteries are suitable for use in motherboards because of their reliability.
- Reputation: A highly respected global brand and often a top choice for coin batteries.
- Panasonic CR2032
- Pros: Panasonic provides high-quality batteries with a good lifespan. This battery is known to be durable and has stable performance.
- Reputation: One of the world’s leading electronics brands with battery products trusted by many users.
- Sony CR2032
- Pros: Batteries from Sony offer reliable performance and a fairly long lifespan. These batteries are often used in a variety of electronic devices.
- Reputation: A leading brand in the electronics industry with recognized battery quality.
- Maxell CR2032
- Pros: Maxell produces reliable batteries and has a good service life. These batteries are also a popular choice for motherboards.
- Reputation: Known as one of the leading battery manufacturers with frequently recommended products.
Conclusion
The coin battery on the motherboard plays a very important role in maintaining the basic functions of the computer.
To ensure your computer is functioning optimally and avoid unwanted problems, it is essential to perform regular maintenance and checks on the coin battery on the motherboard:
By paying attention to regular maintenance and checks, you can ensure that the coin battery on your motherboard is in good working order, keeping your computer stable and operational. This will help avoid interruptions caused by reset BIOS/UEFI settings or inaccurate time and date so that your computer can work efficiently and unhindered.


