Taking user input in batch scripts is a fundamental skill for creating interactive Windows automation programs. This technique allows your scripts to become more dynamic by accepting data directly from users through the command line. In this tutorial, we will explore effective methods of using the SET /P command to handle batch script user input with various practical examples.
Understanding Input Concepts in Batch Scripts
Batch scripts support command line arguments where parameters can be passed during execution. However, certain situations require real-time interaction with users. This is where the role of SET /P becomes crucial for flexible input handling.
The /P switch enables variable assignment based on user-entered input. This feature is particularly useful for scenarios requiring interactivity, such as runtime configuration or dynamic data input.
Basic Implementation of SET /P for User Input
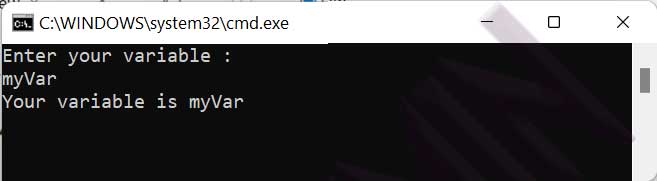
Here’s a fundamental demonstration of using SET /P in batch scripts to receive keyboard input:
@echo off echo Enter your variable: set /p variable= echo Your variable is %variable%
Optimizing User Input Script
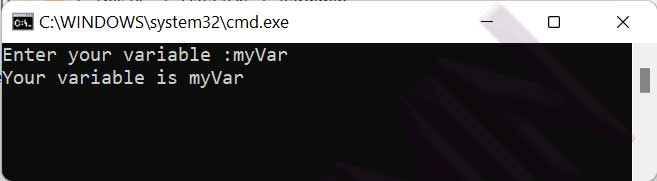
You can simplify the previous code by combining the prompt directly in the SET /P command. This approach results in more efficient and concise scripts.
@echo off SET /P variable=Enter your variable: echo Your variable is %variable%
Practical Applications of Batch Script User Input
In production environments, batch script user input is frequently used for various automation purposes. Here’s an advanced implementation example for configuration management:
@echo off SET /P username=Enter username: SET /P password=Enter password: echo Configuring system for %username%
This technique is highly beneficial for custom installation scripts or system configurations requiring specific parameters from users. Additionally, this approach significantly enhances your script’s flexibility.
Best Practices and Security Considerations
Although SET /P is very powerful, there are several important considerations. Input validation is a critical aspect to prevent unexpected behavior. Always implement checks on user input before further processing.
For security purposes, avoid storing sensitive data like passwords in plain text. Consider using encryption techniques or alternative authentication methods for sensitive information.
By mastering batch script user input techniques, you can create more adaptive and powerful automation solutions. Practice the examples above and experiment with variations according to your specific needs.


