This article discusses a Windows-based data protection solution to counter ransomware attacks by utilizing the Controlled Folder Access feature. You will learn how it works, updated configuration steps, and additional strategies to safeguard critical files from forced encryption threats.
Ransomware is a dangerous type of malware that threatens data security. This software infects systems and encrypts victim’s files. A ransomware attack can cripple business operations and cause significant financial loss. Victims cannot access their own data. To obtain the decryption key, attackers typically demand a ransom in digital currency. However, there is no guarantee the key will be provided after payment.
Relying on a single antivirus solution is often insufficient. The ransomware threat continously evolves with new variants. Therefore, a layered security approach is required. One effective strategy is to restrict write access to important folders. Controlled Folder Access (CFA) is a built-in Windows security feature designed for this purpose. This feature is part of the Windows Security suite.
This feature works by blocking unauthorized modifications. CFA only allows trusted applications to modify files in protected folders. Other applications not on the allow list will be blocked. Thus, ransomware attempts to encrypt data can be prevented from the start. Proper configuration is crucial for balancing security and productivity.
Steps to Enable and Configure Controlled Folder Access
Here is a technical guide to enable and set up the Controlled Folder Access feature on Windows 10 and 11. Ensure your operating system is updated for the best protection.
1. Access Windows Security
Open the Windows Security app. You can search for it via the Start Menu. Then, select the “Virus & threat protection” menu. Scroll down until you find the “Ransomware protection” section. Click on the “Manage ransomware protection” option.
2. Enable Controlled Folder Access
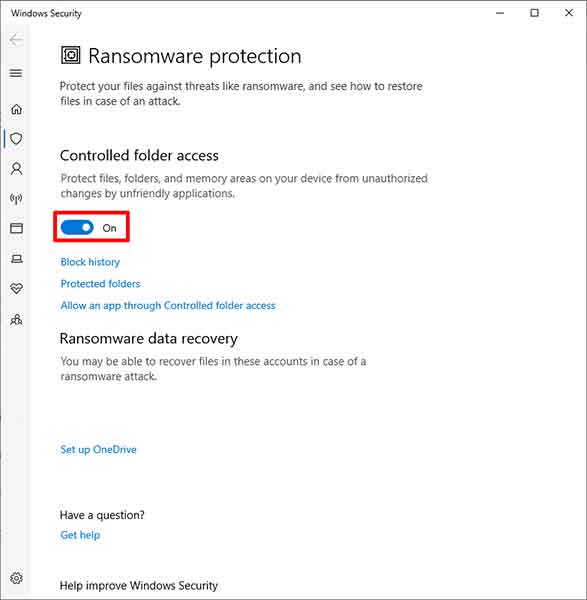
In the next settings window, you will see a toggle switch for Controlled Folder Access. Slide the toggle to “On” to enable it. The system will immediatly start basic protection. However, you need to perform further configuration.
3. Add Folders to Protect
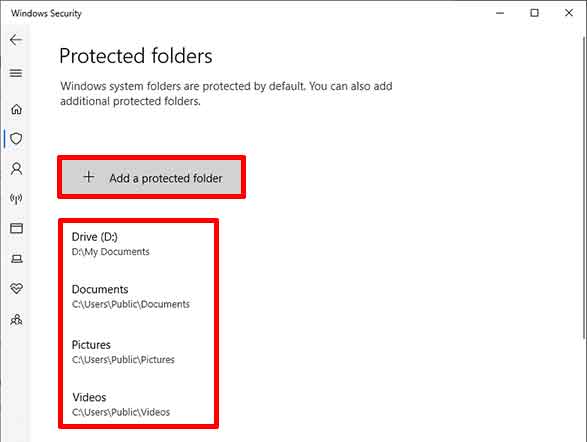
Click the “Protected folders” link. By default, important folders like Documents, Pictures, and Desktop are already protected. To add a custom folder, click “Add a protected folder”. Choose a folder from your desired directory. Try to only protect folders containing critical data.
Professional Tip: Avoid protecting system folders or application installation directories. This can interfere with system performance and software updates.
4. Grant Permission to Trusted Applications
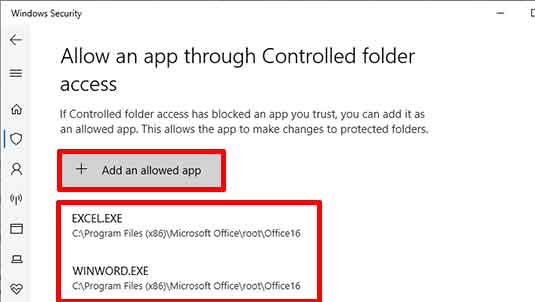
This feature blocks all applications by default. Therefore, you must manually grant permissions. Click the “Allow an app through Controlled folder access” option. Next, click the “Add an allowed app” button. You can add applications like Microsoft Word, Photoshop, or other editor software. Additionally, you can manage permissions via “Block history”. There, you can see blocked applications and allow them if they are trusted.
Additional Strategies for Ransomware Data Protection
Although Controlled Folder Access is powerful, it is not a standalone solution. Implement the following strategies for layered defense. First, always follow the 3-2-1 backup rule. That is, three copies of data, on two different media, with one copy offsite. Second, regularly update the operating system and all applications. Many attacks exploit patched security vulnerabilities.
Third, use user accounts with the principle of least privilege. Do not use an administrator account for daily activities. Fourth, increase vigilance against phishing emails and suspicious links. Security awareness training for the entire team is essential. For more in-depth information on cybersecurity best practices, you can refer to guidelines from the CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency).
By combining the Controlled Folder Access feature with other proactive strategies, the risk of a ransomware attack can be significantly reduced. Configure carefully and test its impact on daily workflow. Data security is an ongoing process requiring regular evaluation and adjustment.


