For professionals and gamers, the need for flexible and reliable connectivity is crucial. The integrated Mobile Hotspot feature in Windows 10 and 11 provides an elegant solution for sharing your PC’s or laptop’s internet connection with other devices, without requiring additional software. This article provides a comprehensive guide, from GUI to command-line methods, plus troubleshooting to ensure an optimal connection sharing experience.
The Mobile Hotspot feature leverages your system’s Wi-Fi Adapter to create a local wireless network. The primary requirement is that the Wi-Fi adapter must support a virtual hosted network. This feature is extremely useful for emergencies, presentations, or when you need a more stable network for a gaming console or IoT devices.
How to Create a Hotspot via Windows Settings (GUI)
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) method is the most intuitive way to activate the hotspot. Follow these systematic steps.
- Open Settings by pressing the Start button and selecting the gear icon, or by using the keyboard shortcut
Windows Key + I.
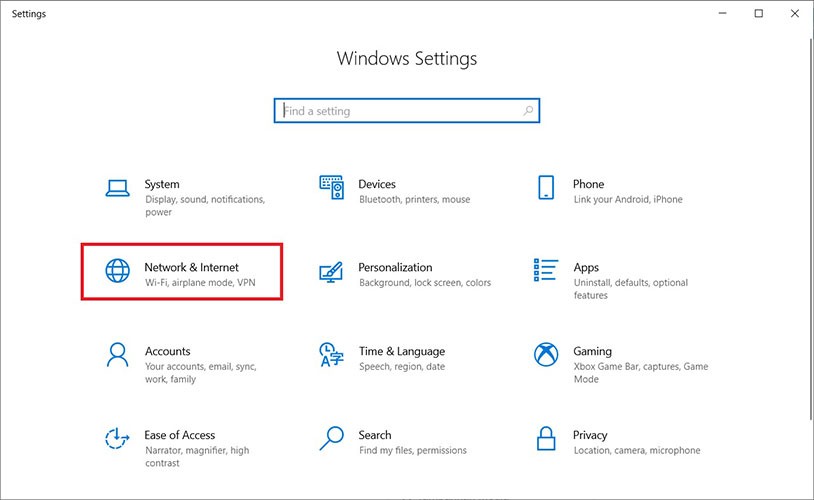
- In the Settings window, select the Network & Internet menu, then click on Mobile hotspot from the left-hand panel.
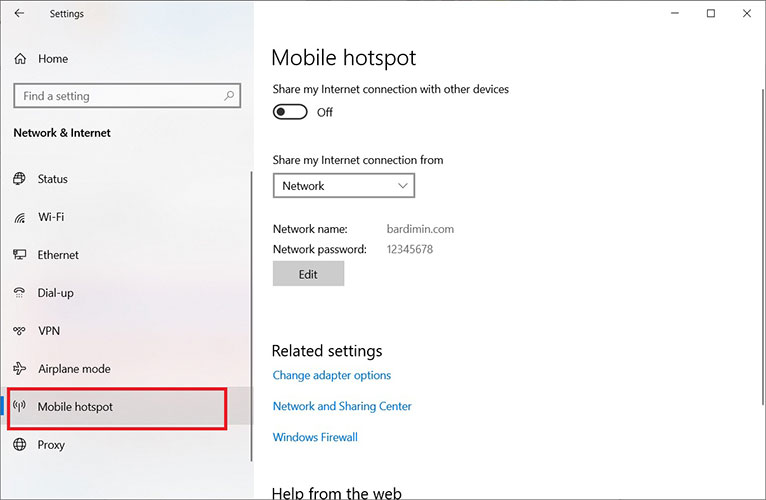
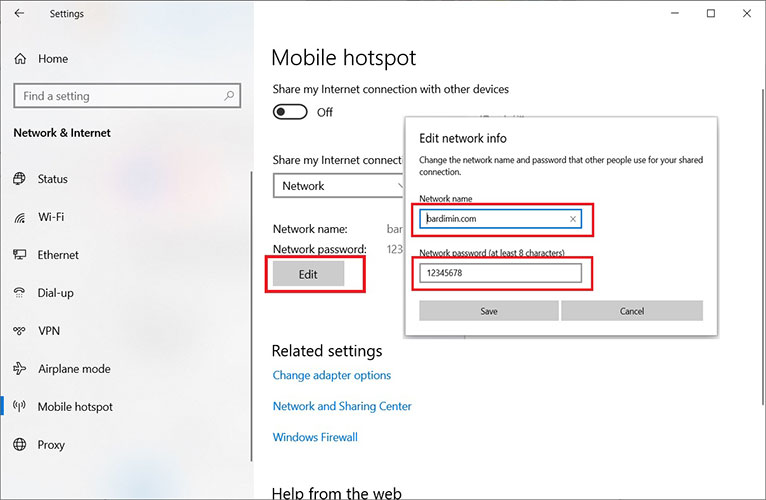
- Click the Edit button to configure the SSID (network name) and Network password. Use a strong password (minimum 8 characters, combining letters, numbers, and symbols).
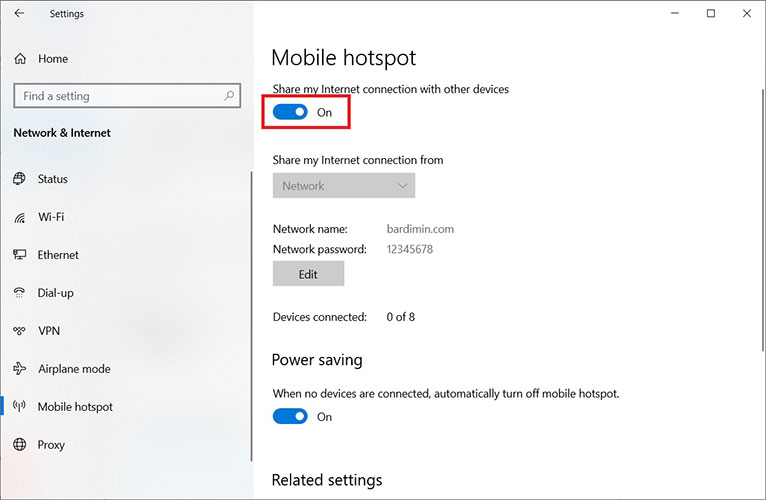
- In the “Share my Internet connection from” section, ensure the correct source connection is selected (Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or cellular). Finally, toggle the Share my Internet connection with other devices switch to the ‘On’ position.
Advanced Method: Creating a Hotspot via Command Prompt
For technicians requiring automation or more granular control, using the netsh command in Command Prompt (run as Administrator) is the solution.
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=YourHotspotName key=YourPassword
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
After running these commands, you must share your primary internet connection with the newly created virtual network via Network Connections in the Control Panel.
Common Windows Hotspot Troubleshooting
- Adapter Not Supported: Use the command
netsh wlan show driversand check the “Hosted network supported” line. If it says “No”, your Wi-Fi adapter is not compatible. - Devices Cannot Connect: Ensure Airplane mode is off and check your firewall settings to ensure the connection isn’t being blocked.
- Hotspot Won’t Turn On: Reset the network stack by running Command Prompt (Admin) and typing:
netsh winsock resetthen restart your computer.
By understanding both the GUI and CLI methods, along with basic troubleshooting techniques, you can ensure a stable and secure hotspot connection to support your productivity and gaming activities.


