Wir hören oft die Begriffe BIOS und UEFI. Aber wissen Sie, wie BIOS und UEFI funktionieren?
Die meisten Computernutzer wissen nur, dass vor dem Einschalten des Computers eine Anzeige der Hardware-Informationen erscheint, d. h. ein Bericht über die Ergebnisse des BIOS/UEFI, bevor der Computer das Betriebssystem lädt.
Difference between BIOS and UEFI
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System and is also known as system BIOS, ROM BIOS, or PC BIOS. While the definition of BIOS is the firmware used to initialize the hardware during the boot process (power-on startup), and to provide runtime services for the operating system and programs.
The BIOS firmware is pre-installed on the computer’s motherboard and is the first software that runs when the computer is turned on.
The BIOS is stored in an EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) which allows the manufacturer to perform updates easily.
You can access the BIOS by pressing del, F2 or F10 during the initial phase of the boot procedure
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, or what we usually call UEFI, is the software between the operating system and firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface that was originally on all computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services.
UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even without an operating system installed.
BIOS and UEFI have the same task, namely initializing hardware components and starting the operating system stored on the hard disk drive when the computer starts up.
The main difference between UEFI and BIOS is that UEFI stores all data about initialization and startup in an .efi file, while BIOS stores it in firmware.
This .efi file is stored in a special partition called EFI System Partition (ESP) on the hard disk. This ESP partition also contains the bootloader.
Advantages of using UEFI
UEFI came as a refinement of the shortcomings of the BIOS. As a BIOS enhancement, of course, UEFI has many advantages over its predecessors. Some of the advantages of UEFI, among others:
- UEFI supports drive and partition sizes up to 8 ZB (zettabyte), while BIOS only supports 2 TB (terabyte).
- UEFI supports an unlimited number of partitions, whereas BIOS can only create 4 primary partitions.
- Boot time using EUFI is faster.
- UEFI offers „Secure Boot“ security to prevent the computer from booting from unauthorized applications and to ensure that no malware interferes with the startup process .
- UEFI supports network functions in the UEFI firmware itself, which helps remote troubleshooting and the UEFI configuration.
- UEFI runs in 32bit or 64bit mode, which can provide GUI navigation with a mouse, while BIOS runs in 16bit mode and navigates using only the keyboard.
So überprüfen Sie Windows im UEFI- oder Legacy-BIOS-Modus
1. Öffnen Sie „System Information“.
Klicken Sie auf Suchen und geben Sie „System Information“ ein. Wählen Sie dann die Anwendung “ System Information „.
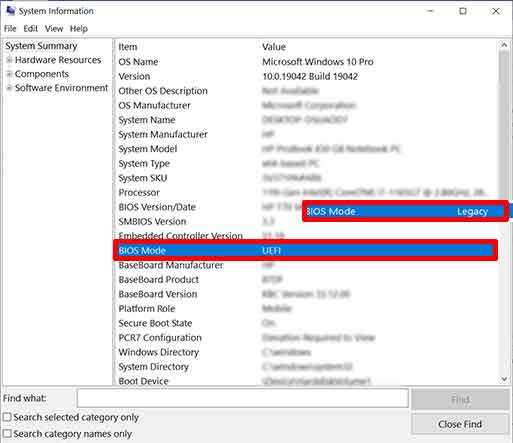
2. Prüfen Sie den Punkt „BIOS Mode“.
Wenn der Eintrag „BIOS Mode“ „UEFI“ lautet, bedeutet dies, dass Sie den UEFI-Boot-Modus verwendet haben. Wenn der Wert „Legacy“ lautet, bedeutet dies, dass Sie noch den Legacy-BIOS-Boot-Modus verwenden.
Wie ändert man den Bootmodus von Legacy BIOS zu UEFI unter Windows ohne Neuinstallation und Datenverlust
Sie können die folgenden Schritte verwenden, um das Legacy-BIOS auf allen Versionen von Windows 11 und Windows 10 mit einer Mindestversion von 1703 in UEFI zu ändern.
